2025-12-22 マウントサイナイ医療システム(MSHS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/ai-could-help-predict-nutrition-risks-in-icu-patients-study-finds
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-66200-1
NutriSighT: 人工呼吸器患者の経腸栄養不足の動的予測のための解釈可能なトランスフォーマーモデル NutriSighT: Interpretable Transformer Model for Dynamic Prediction of Underfeeding Enteral Nutrition in Mechanically Ventilated Patients
Mateen Jangda,Jayshil Patel,Akhil Vaid,Jaskirat Gill,Paul McCarthy,Jacob Desman,Rohit Gupta,Dhruv Patel,Nidhi Kavi,Shruti Bakare,Eyal Klang,Robert Freeman,Anthony Manasia,John Oropello,Lili Chan,Mayte Suarez-Farinas,Alexander W. Charney,Roopa Kohli-Seth,Girish N. Nadkarni & Ankit Sakhuja
Nature Communications Published:17 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-66200-1
Abstract
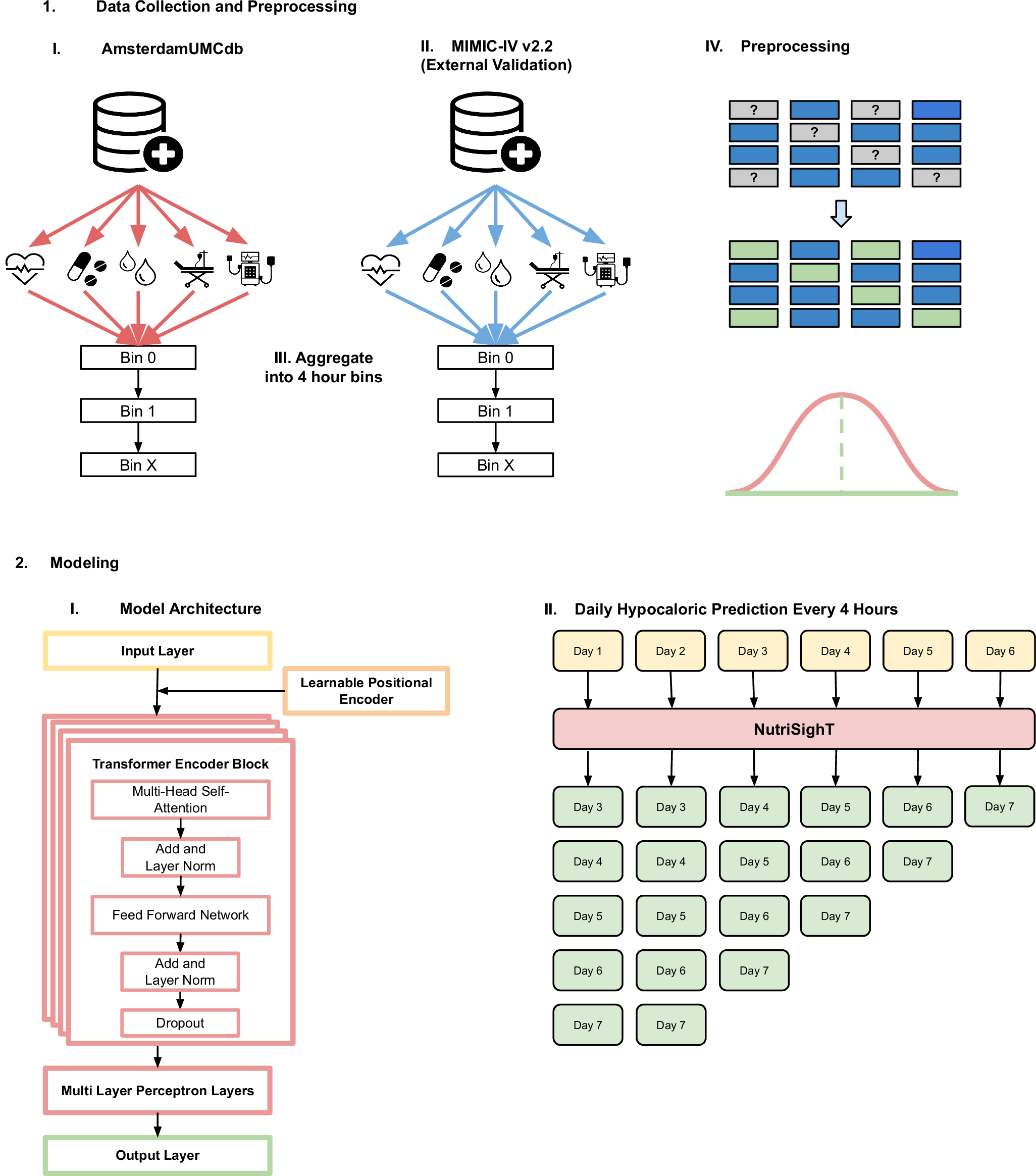
Achieving adequate enteral nutrition among mechanically ventilated patients is challenging, yet critical. We develop NutriSighT, a transformer model using learnable positional encodings to predict which patients would be underfed (receive less than 70% daily caloric requirements) between days 3-7 of mechanical ventilation and compared its performance against XGBoost. Using retrospective data from two ICU databases (3284 patients from AmsterdamUMCdb for development and 6456 from MIMIC-IV for external validation), we included adults mechanically ventilated for at least 72 h. NutriSighT achieved AUROC of 0.81 (95% CI: 0.81 – 0.82) and AUPRC of 0.70 (95% CI: 0.70 – 0.72) internally. External validation yielded AUROC of 0.76 (95% CI: 0.75 – 0.76) and an AUPRC of 0.70 (95% CI: 0.69 – 0.70). In comparison, XGBoost achieved AUROC of 0.58 (95% CI: 0.58 – 0.59) and AUPRC of 0.48 (95% CI: 0.46 – 0.50). This approach may help clinicians personalize nutritional therapy in critical care.