2026-01-13 大阪大学
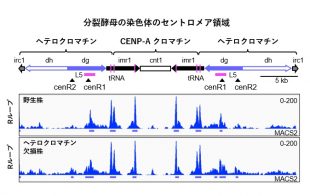
DRIP-Seq法によるRループの検出
<関連情報>
- https://www.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/topics/16250/
- https://www.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/pr_nakagawa_1.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/54/1/gkaf1455/8418231
セントロメリック反復における転写PBRサイクルは、Rad52依存性ADRループ形成を介して染色体再編成を引き起こす Transcriptional PBR cycles at pericentromeric repeats cause gross chromosomal rearrangements through Rad52-dependent ADR-loop formation
Ran Xu,Crystal Tang,Jianfang N Wang,Daisuke Motooka,Hideo Tsubouchi,Hiroshi Iwasaki,Takuro Nakagawa
Nucleic Acids Research Published:13 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf1455
Abstract
Heterochromatin marked by histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methylation represses transcription of pericentromeric repeats, thereby suppressing gross chromosomal rearrangements (GCRs). However, it remains unclear how transcription causes GCRs when heterochromatin is lost. Using fission yeast, we show that transcriptional Pausing–Backtracking–Restart (PBR) cycles accumulate R-loops, leading to GCRs. DNA–RNA immunoprecipitation (DRIP) revealed that loss of Clr4, the H3K9 methyltransferase, increased R-loops at pericentromeric repeats. Overexpression of RNaseH1 in clr4∆ cells reduced both R-loops and GCRs, demonstrating that R-loops cause GCRs. Tfs1/TFIIS and Ubp3, required for transcriptional restart, and Seb1, involved in pausing at pericentromeres, were required for R-loop accumulation and GCRs, implicating PBR cycles in the formation of genotoxic R-loops. We also demonstrate that Rad52 recombinase localizes to pericentromeric repeats and facilitates GCRs in clr4∆ cells. rad52–R45K, which impairs single-strand annealing (SSA), reduced GCRs. A single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) region within an R-loop may anneal to homologous ssDNA to form Annealing-induced DNA–RNA-loops (ADR-loops). Indeed, Rad52 facilitated ADR-loop formation in vitro. Polδ was also involved in GCRs. These data suggest that, when heterochromatin is lost, transcriptional PBR cycles accumulate R-loops at pericentromeric repeats, and Rad52-dependent SSA converts R-loops into ADR-loops followed by Polδ-dependent break-induced replication (BIR), resulting in homology-mediated GCRs.