2026-01-15 東京科学大学
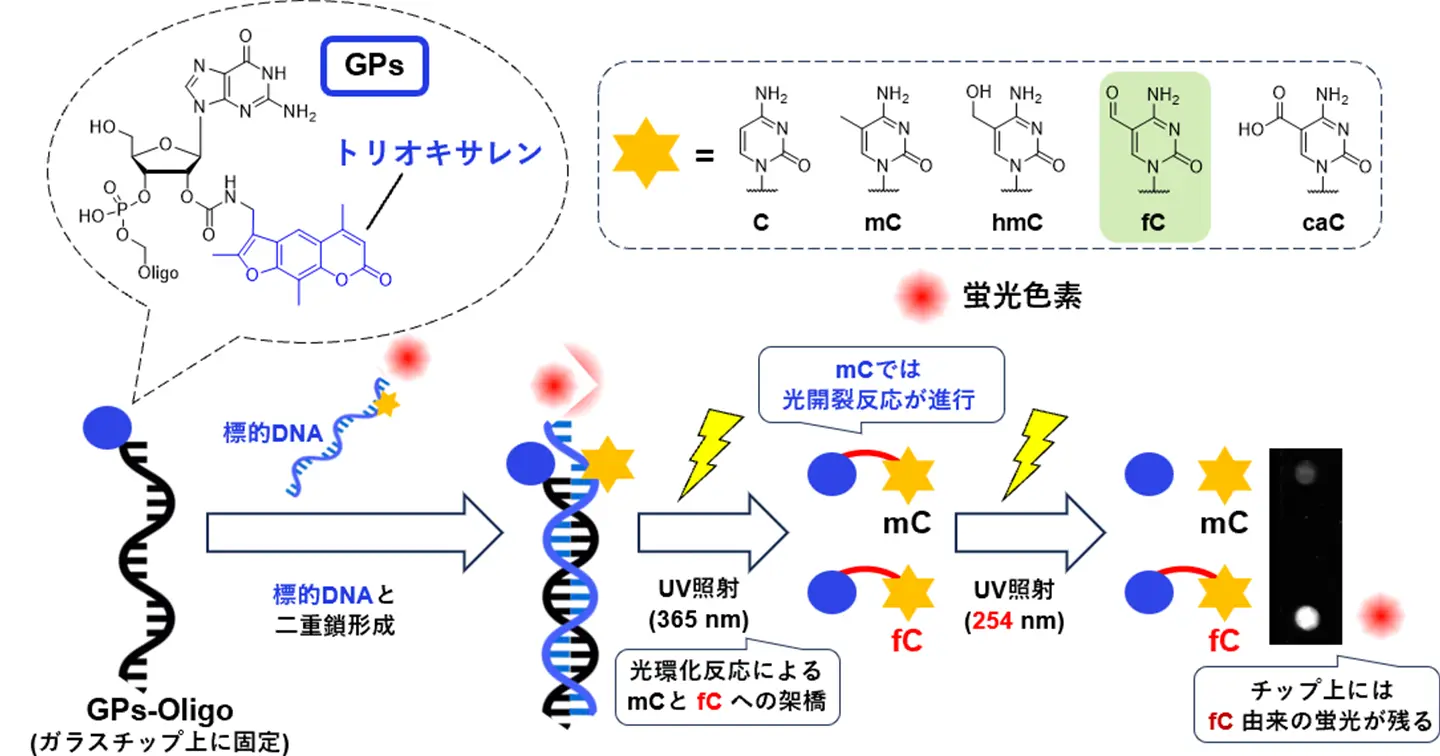
図1. 開発した光架橋性分子プローブ(GPs-Oligo)を用いたDNAチップ上での5fCの検出
<関連情報>
トリオキサレン結合グアノシンを含む新規光反応性オリゴヌクレオチドを用いたエピジェネティックに重要な5-ホルミルシトシン修飾の検出 Detection of Epigenetically Important 5-Formylcytosine Modifications Using Novel Photoreactive Oligonucleotides Containing a Trioxsalen-Conjugated Guanosine
Yu Mikame,Hiroaki Shirahama,Kinuka Doi,Nagisa Maekawa,Hiroki Kanazawa,Tsuyoshi Yamamoto,Chikara Dohno,Jiro Kondo,Takehiko Wada,and Asako Yamayoshi
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: January 7, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c11463
Abstract
Transcription is tightly regulated by epigenetic modifications that control the expression of specific genes. One such modification is 5-methylcytosine (5mC) that is formed by cytosine methylation via DNA methyltransferases and functions as a transcriptional silencer of gene promoters. Dynamically regulated subsequent modifications by ten–eleven translocation (TET) enzymes catalyze the sequential oxidation of 5mC for generating 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine. Recently, these oxidized cytosine derivatives were indicated as not merely intermediates in the demethylation process; however, each derivative plays a unique biologically relevant role. A photo-crosslinkable oligonucleotide probe for detecting these cytosine modifications could support the spatiotemporal functional analysis of cytosine derivatives via a light stimulus. Herein, we designed novel photoreactive nucleosides by conjugating a psoralen (Ps) derivative, trioxsalen, to the C2′ position of guanosine (GPs and GPs2) and developed photo-crosslinkable oligonucleotides (GPs–Oligo and GPs2–Oligo). In particular, GPs–Oligo demonstrated an intriguing and unique ability of photo-crosslinking with 5fC. GPs–Oligo was employed to detect 5fC using a DNA chip glass plate, which demonstrated the potential of GPs–Oligo for future investigation of the function of 5fC inside cells.