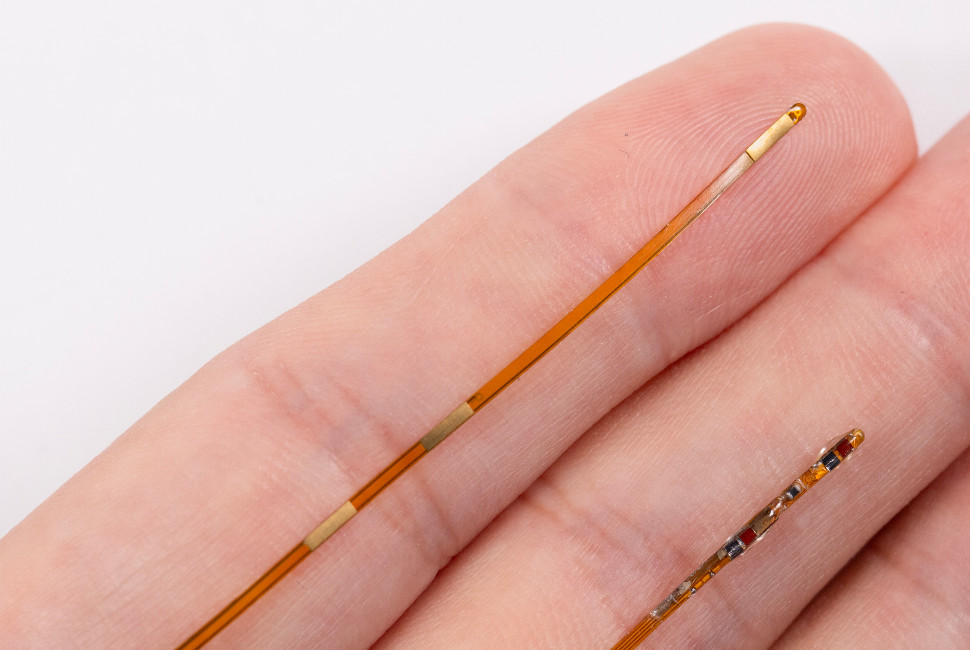
2026-01-26 理化学研究所,,東京科学大学,日本医科大学

白血病の免疫を維持する記憶タンパク質と白血病細胞の抗体のT細胞エンジニアリング
<関連情報>
- https://www.riken.jp/press/2026/20260126_2/index.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-67745-x
CXCR4はCAR-T細胞の疲弊に対する記憶形成を誘導し、持続的な白血病標的化を実現する CXCR4 induces memory formation over exhaustion in CAR-T cells to achieve durable leukemia targeting
Ari Itoh-Nakadai,Minggao Liang,Michiho Shindo,Chen Bibi,Mariko Tomizawa-Murasawa,Saera Fujiki,Akiko Kaneko,Emi Kanamaru,Mari Hashimoto,Hiroshi Kajita,Yoshinari Ando,Miki Kojima,Jonathan Moody,Makoto Iwasaki,Shinsuke Takagi,Ryo Nakagawa,Saumya Agrawal,Hanae Amitani-Iijima,Kaori Sato,Yuriko Sorimachi,Nahoko Suzuki,Takehiro Fukami,Kazuharu Hanada,Satoshi Morita,… Fumihiko Ishikawa
Nature Communications Published:26 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67745-x
Abstract
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has transformed the treatment of B-cell malignancies, but its success in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains limited. Durable responses depend on the formation of long-lived memory T cells, whereas T cell exhaustion contributes to non-response and relapse. In patients with AML who achieved remission after cord blood transplantation, we here first observe enrichment of memory T cells with high expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Next, we show that engineering CAR-T cells to co-express CXCR4 enhances their persistence and anti-leukemic activity in patient-derived xenograft models. Using single-cell profiling and metabolic analysis, we find that CXCR4 promotes memory-associated transcriptional programs, reduces exhaustion, and supports oxidative metabolism. These effects are observed with CAR-T cells targeting CD25 or CD96 as AML-associated targets. Our results indicate that CXCR4 strengthens CAR-T cell memory and durability, offering a strategy to improve immunotherapy outcomes in AML and beyond.