タンパク質の大規模な検査でバイオマーカーの可能性を発見 Large Scale Protein Exam Leads to Potential Biomarkers
2022-05-04 ヒューストン大学(UH)
ヒューストン大学生体工学部准教授のTianfu Wuは、「SLE/LN患者の精密診断と個別化治療のための分類における異質性とアンメットニーズを考えると、新規バイオマーカー、特にバイオマーカーパネルの特定が最も重要です」と、雑誌「Frontiers in Immunology」で報告しています。
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2022-news-articles/may-2022/05042022-lupus-nephritis-biomarkers-proteins-tianfu-wu.php
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.850015/full
イムノプロテオミクスによるループス腎炎における新規循環型免疫複合体の発見 Discovery of Novel Circulating Immune Complexes in Lupus Nephritis Using Immunoproteomics
Chenling Tang, Min Fang, Gongjun Tan, Shu Zhang, Bowen Yang, Yaxi Li, Ting Zhang, Ramesh Saxena, Chandra Mohan and Tianfu Wu
Frontiers in Immunology Published:24 March 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.850015
Abstract
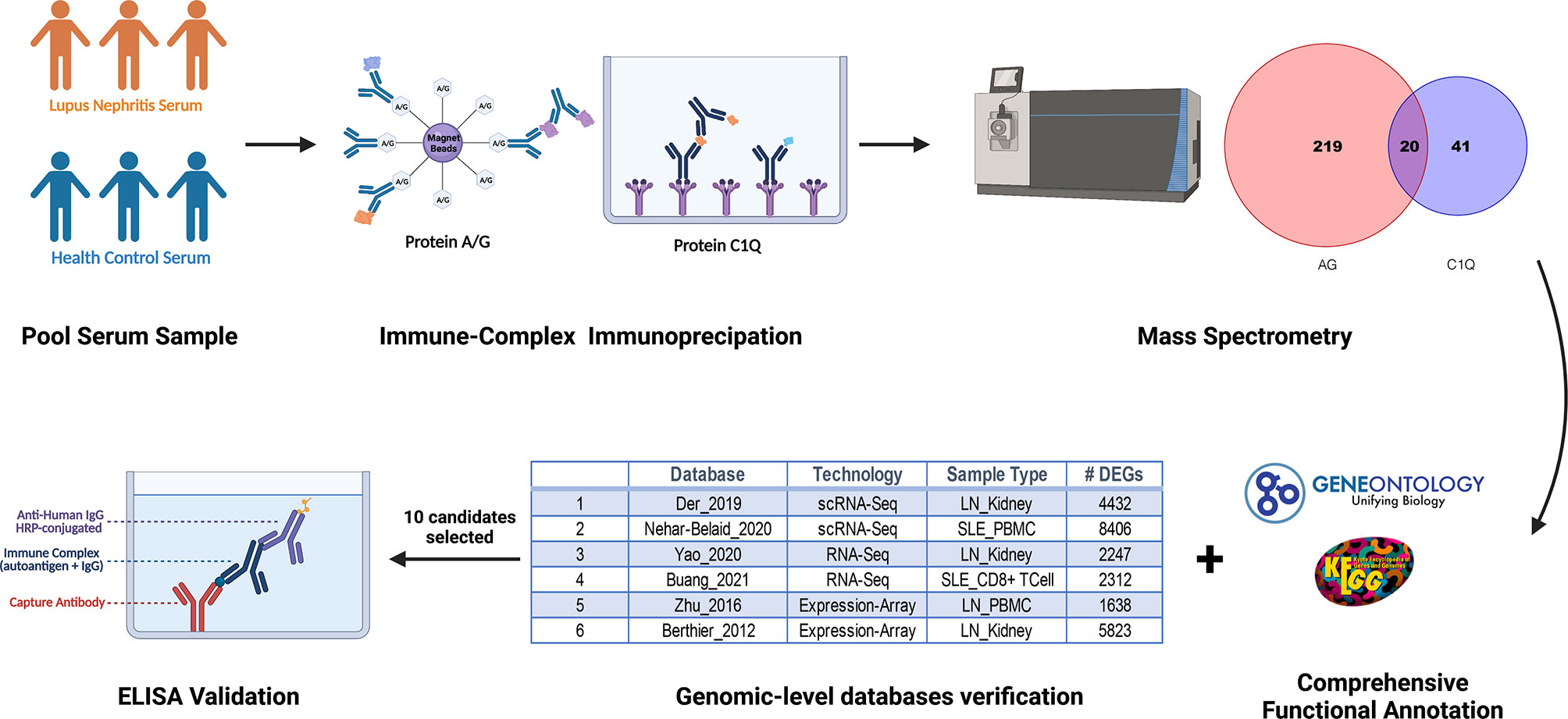
Objective: The goal is to discover novel circulating immune complexes (ICx) in the serum of lupus nephritis (LN) as potential biomarkers.
Methods: Protein A/G magnetic beads or C1q-coated plates were used to capture ICx in the serum of LN, followed by the identification of immunoglobulin-binding proteins using liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Bioinformatic approaches and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA Seq) databases were used to select potential candidate ICx markers in LN. The selected ICx markers were further validated using ELISA.
Results: A total of 300 immunoglobulin-binding proteins were discovered in the screening, among which 77 proteins were detectable only in LN samples. Bioinformatics-assisted selection allowed us to further identify 10 potential immunoglobulin-binding proteins, which form ICx as potential biomarkers in LN. In a validation cohort of 62 LN patients and 21 healthy controls (HC), we found that prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 (P3H1), phosphatase and actin regulator 4 (PHACTR4), and regulator of G-protein signaling 12 (RGS12) ICx exhibited discriminative capability in distinguishing LN from HC, with an area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.82, 0.99, and 0.90, respectively. Furthermore, a biomarker panel comprising CD14, CD34, cystatin A, myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C), RGS12, and ubiquitin C (UBC) ICx could distinguish active LN from inactive LN with an AUC value of 0.85, which is comparable to or better than pathological parameters such as renal activity index (AI) and renal chronicity index (CI).
Conclusion: Immunoproteomics-based discovery studies have enabled us to identify circulating immune complexes as potential biomarkers of LN.