2023-05-22 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
◆この方法は5PSeqと呼ばれ、メッセンジャーRNA(mRNA)のシーケンシングに基づいています。研究者たちは、この方法を使ってさまざまな種類の細菌をテストし、抗生物質への反応を数分で判定できることを確認しました。
◆彼らはこの方法を簡便な検査として医師が利用できるように開発することを目指しています。これにより、適切な抗生物質の迅速な選択が可能となり、抗生物質耐性の問題に取り組む一助となることが期待されています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/new-method-reveals-bacterial-reaction-to-antibiotics-in-five-minutes
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-023-01393-z
バクテリアのmRNA翻訳と崩壊のアトラス Atlas of mRNA translation and decay for bacteria
Susanne Huch,Lilit Nersisyan,Maria Ropat,Donal Barrett,Mengjun Wu,Jing Wang,Valerie D. Valeriano,Nelli Vardazaryan,Jaime Huerta-Cepas,Wu Wei,Juan Du,Lars M. Steinmetz,Lars Engstrand & Vicent Pelechano
Nature Microbiology Published:22 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01393-z
Abstract
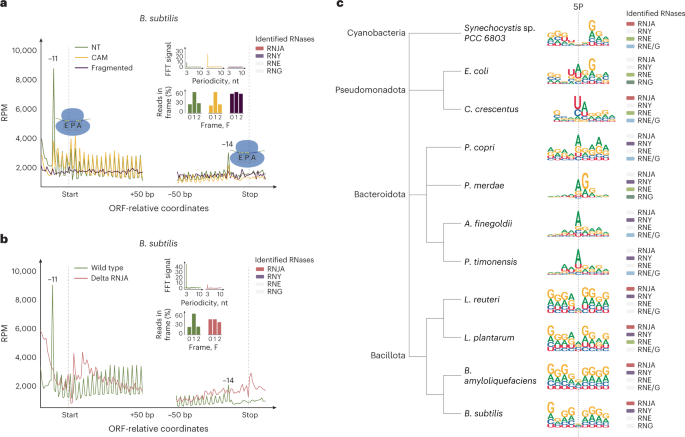
Regulation of messenger RNA stability is pivotal for programmed gene expression in bacteria and is achieved by a myriad of molecular mechanisms. By bulk sequencing of 5′ monophosphorylated mRNA decay intermediates (5′P), we show that cotranslational mRNA degradation is conserved among both Gram-positive and -negative bacteria. We demonstrate that, in species with 5′–3′ exonucleases, the exoribonuclease RNase J tracks the trailing ribosome to produce an in vivo single-nucleotide toeprint of the 5’ position of the ribosome. In other species lacking 5′–3′ exonucleases, ribosome positioning alters endonucleolytic cleavage sites. Using our metadegradome (5′P degradome) sequencing approach, we characterize 5′P mRNA decay intermediates in 96 species including Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Synechocystis spp. and Prevotella copri and identify codon- and gene-level ribosome stalling responses to stress and drug treatment. We also apply 5′P sequencing to complex clinical and environmental microbiomes and demonstrate that metadegradome sequencing provides fast, species-specific posttranscriptional characterization of responses to drug or environmental perturbations. Finally we produce a degradome atlas for 96 species to enable analysis of mechanisms of RNA degradation in bacteria. Our work paves the way for the application of metadegradome sequencing to investigation of posttranscriptional regulation in unculturable species and complex microbial communities.