2023-10-04 ジョージア工科大学
◆研究者は物理モデルとロボティクスを使用して、これらの飛行モードの移行がどのように発生するかを調査しました。この研究は異なる学際領域の専門知識と協力によって成し遂げられ、昆虫の動きを理解し、ロボットシステムに応用するための重要な知見を提供しています。
<関連情報>
- https://research.gatech.edu/feature/ultrafast-flight
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06606-3
進化、生理学、ロボット物理学における昆虫の2つの飛行モードの架け橋 Bridging two insect flight modes in evolution, physiology and robophysics
Jeff Gau,James Lynch,Brett Aiello,Ethan Wold,Nick Gravish & Simon Sponberg
Nature Published:04 October 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06606-3
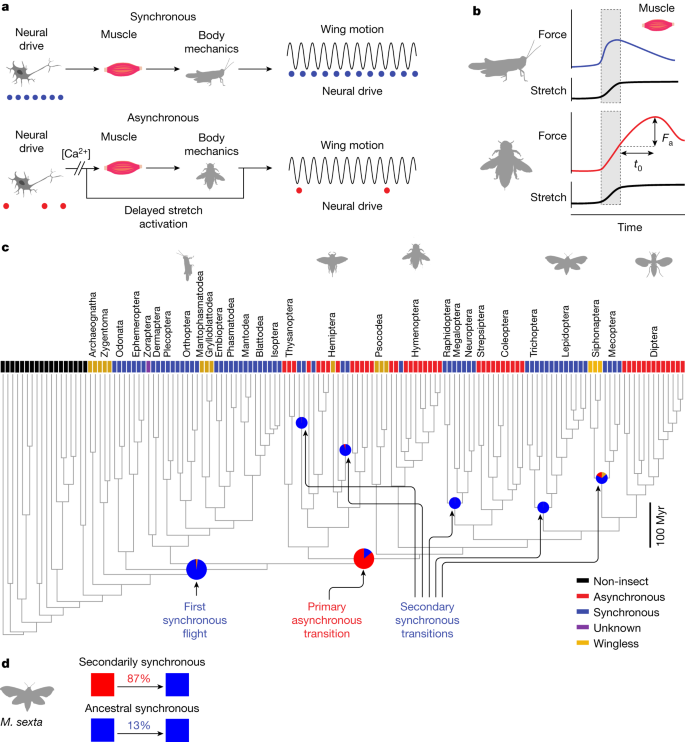
Abstract
Since taking flight, insects have undergone repeated evolutionary transitions between two seemingly distinct flight modes1,2,3. Some insects neurally activate their muscles synchronously with each wingstroke. However, many insects have achieved wingbeat frequencies beyond the speed limit of typical neuromuscular systems by evolving flight muscles that are asynchronous with neural activation and activate in response to mechanical stretch2,3,4,5,6,7,8. These modes reflect the two fundamental ways of generating rhythmic movement: time-periodic forcing versus emergent oscillations from self-excitation8,9,10. How repeated evolutionary transitions have occurred and what governs the switching between these distinct modes remain unknown. Here we find that, despite widespread asynchronous actuation in insects across the phylogeny3,6, asynchrony probably evolved only once at the order level, with many reversions to the ancestral, synchronous mode. A synchronous moth species, evolved from an asynchronous ancestor, still preserves the stretch-activated muscle physiology. Numerical and robophysical analyses of a unified biophysical framework reveal that rather than a dichotomy, these two modes are two regimes of the same dynamics. Insects can transition between flight modes across a bridge in physiological parameter space. Finally, we integrate these two actuation modes into an insect-scale robot11,12,13 that enables transitions between modes and unlocks a new self-excited wingstroke strategy for engineered flight. Together, this framework accounts for repeated transitions in insect flight evolution and shows how flight modes can flip with changes in physiological parameters.


