2024-01-16 ワシントン州立大学(WSU)
◆特に、大麻がカンナビノイド-1受容体を介して摂食細胞を制御し、その活動を促進することが示されました。この発見は、がん患者や拒食症、肥満などの食欲障害の治療法開発に寄与する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/press-release/2024/01/16/cannabis-activates-specific-hunger-neurons-in-brain/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-50112-5
大麻サティバは食欲を刺激する視床下部の中基底部ニューロンを標的とする Cannabis Sativa targets mediobasal hypothalamic neurons to stimulate appetite
Emma C. Wheeler,Pique Choi,Joanne De Howitt,Sumeen Gill,Shane Watson,Sue Yu,Peyton Wahl,Cecilia Diaz,Claudia Mohr,Amy Zinski,Zhihua Jiang,David Rossi & Jon F. Davis
Scientific Reports Published:27 December 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-50112-5
Abstract
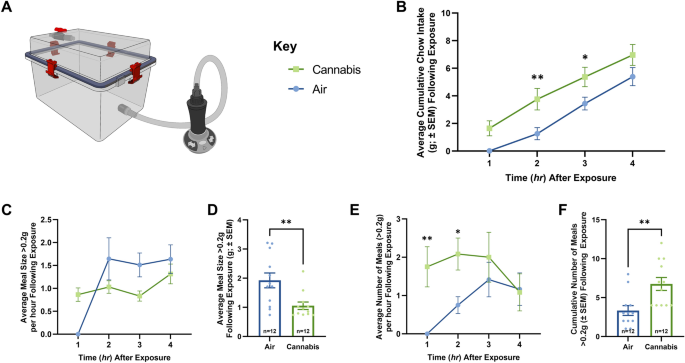
The neurobiological mechanisms that regulate the appetite-stimulatory properties of cannabis sativa are unresolved. This work examined the hypothesis that cannabinoid-1 receptor (CB1R) expressing neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH) regulate increased appetite following cannabis vapor inhalation. Here we utilized a paradigm where vaporized cannabis plant matter was administered passively to rodents. Initial studies in rats characterized meal patterns and operant responding for palatable food following exposure to air or vapor cannabis. Studies conducted in mice used a combination of in vivo optical imaging, electrophysiology and chemogenetic manipulations to determine the importance of MBH neurons for cannabis-induced feeding behavior. Our data indicate that cannabis vapor increased meal frequency and food seeking behavior without altering locomotor activity. Importantly, we observed augmented MBH activity within distinct neuronal populations when mice anticipated or consumed food. Mechanistic experiments demonstrated that pharmacological activation of CB1R attenuated inhibitory synaptic tone onto hunger promoting Agouti Related Peptide (AgRP) neurons within the MBH. Lastly, chemogenetic inhibition of AgRP neurons attenuated the appetite promoting effects of cannabis vapor. Based on these results, we conclude that MBH neurons contribute to the appetite stimulatory properties of inhaled cannabis.