2024-01-16 ノースウェスタン大学
◆この治療法は、特定のアレルギーを選択的に防ぎ、免疫系全体を抑制することなく実現します。マウス実験では、治療法はアレルギー反応を100%防ぎ、顕著な副作用も引き起こさなかったと報告されています。研究はナノテクノロジージャーナルに掲載され、特定のアレルギーに対するマスト細胞の阻害を目指す初のナノ治療法として注目されています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.northwestern.edu/stories/2024/01/decorated-nanoparticles-prevent-allergic-reactions/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01584-z
複数の生理活性タンパク質の吸着を制御することで、肥満細胞を標的としたナノ治療が可能に Controlled adsorption of multiple bioactive proteins enables targeted mast cell nanotherapy
Fanfan Du,Clayton H. Rische,Yang Li,Michael P. Vincent,Rebecca A. Krier-Burris,Yuan Qian,Simseok A. Yuk,Sultan Almunif,Bruce S. Bochner,Baofu Qiao & Evan A. Scott
Nature Nanotechnology Published:16 January 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01584-z
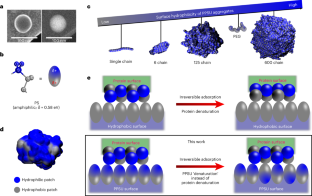
Abstract
Protein adsorption onto nanomaterials often results in denaturation and loss of bioactivity. Controlling the adsorption process to maintain the protein structure and function has potential for a range of applications. Here we report that self-assembled poly(propylene sulfone) (PPSU) nanoparticles support the controlled formation of multicomponent enzyme and antibody coatings and maintain their bioactivity. Simulations indicate that hydrophobic patches on protein surfaces induce a site-specific dipole relaxation of PPSU assemblies to non-covalently anchor the proteins without disrupting the protein hydrogen bonding or structure. As a proof of concept, a nanotherapy employing multiple mast-cell-targeted antibodies for preventing anaphylaxis is demonstrated in a humanized mouse model. PPSU nanoparticles displaying an optimized ratio of co-adsorbed anti-Siglec-6 and anti-FcεRIα antibodies effectively inhibit mast cell activation and degranulation, preventing anaphylaxis. Protein immobilization on PPSU surfaces provides a simple and rapid platform for the development of targeted protein nanomedicines.