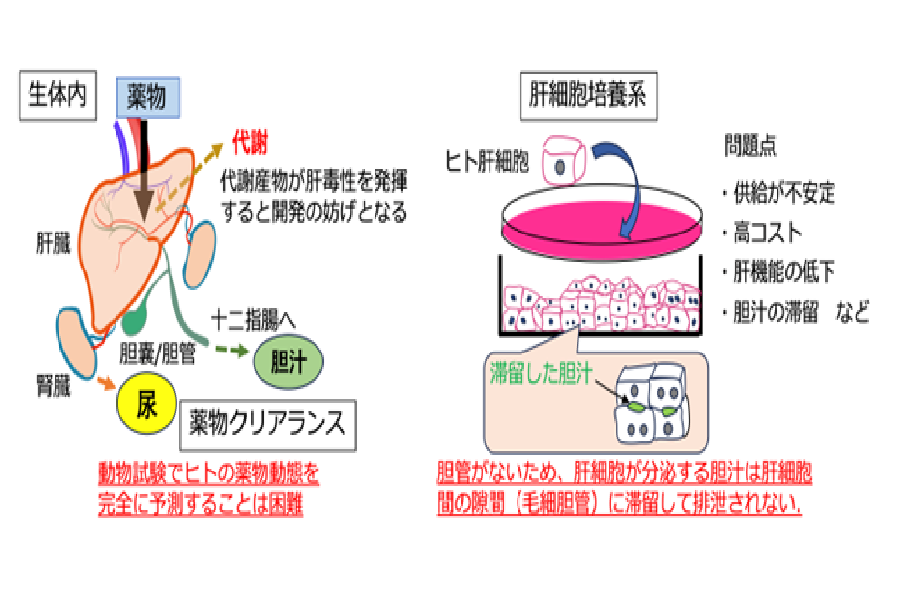
2024-06-04 ワシントン州立大学(WSU)
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/press-release/2024/06/04/protein-discovery-could-help-prevent-cancer-treatment-related-heart-damage/
- https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/cvr/cvae084/7655714
サイクリン依存性キナーゼ7の阻害はドキソルビシンの心毒性を緩和し、抗癌効果を高める Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 mitigates doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and enhances anticancer efficacy
Jingrui Chen, Jing Wei, Peng Xia, Yuening Liu, Mahder Dawit Belew, Ryan Toohill, Boyang Jason Wu, Zhaokang Cheng
Cardiovascular Research Published:22 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvae084
Abstract
Aims
The anthracycline family of anticancer agents such as doxorubicin (DOX) can induce apoptotic death of cardiomyocytes and cause cardiotoxicity. We previously reported that DOX-induced apoptosis is accompanied by cardiomyocyte cell cycle re-entry. Cell cycle progression requires cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7)-mediated activation of downstream cell cycle CDKs. This study aims to determine whether CDK7 can be targeted for cardioprotection during anthracycline chemotherapy.
Methods and results
DOX exposure induced CDK7 activation in mouse heart and isolated cardiomyocytes. Cardiac-specific ablation of Cdk7 attenuated DOX-induced cardiac dysfunction and fibrosis. Treatment with the covalent CDK7 inhibitor THZ1 also protected against DOX-induced cardiomyopathy and apoptosis. DOX treatment induced activation of the proapoptotic CDK2–FOXO1–Bim axis in a CDK7-dependent manner. In response to DOX, endogenous CDK7 directly bound and phosphorylated CDK2 at Thr160 in cardiomyocytes, leading to full CDK2 kinase activation. Importantly, inhibition of CDK7 further suppressed tumour growth when used in combination with DOX in an immunocompetent mouse model of breast cancer.
Conclusion
Activation of CDK7 is necessary for DOX-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiomyopathy. Our findings uncover a novel proapoptotic role for CDK7 in cardiomyocytes. Moreover, this study suggests that inhibition of CDK7 attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity but augments the anticancer efficacy of DOX. Therefore, combined administration of CDK7 inhibitor and DOX may exhibit diminished cardiotoxicity but superior anticancer activity.
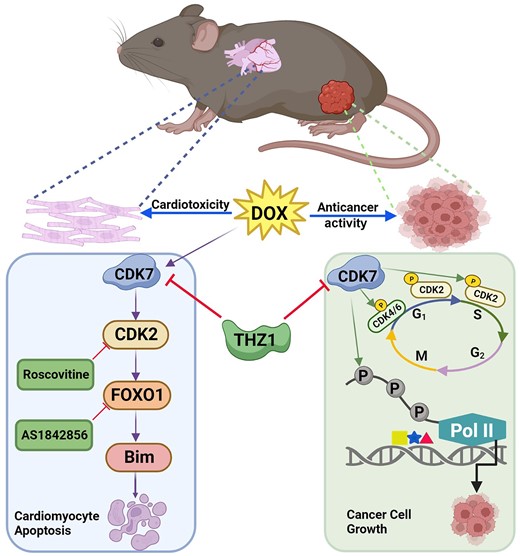
Graphical Abstract