2024-06-07 ノースカロライナ州立大学(NCState)
新しい研究によると、統合失調症や他の精神病性障害と診断された患者は、これらの障害を持たない成人よりも3倍多くバルトネラ菌のDNAを血中に持っていることがわかりました。バルトネラは主にノミやシラミなどの節足動物を介して伝染する細菌で、猫ひっかき病を引き起こすBartonella henselaeを含む、少なくとも45種類が知られています。
◆ノースカロライナ州立大学の研究者は、116人の血液サンプルを分析し、43%の精神病患者がバルトネラ菌のDNAを持っていることを発見しました。これに対して、対照群では14%でした。DNAシーケンシングにより、Bartonella henselae、Bartonella vinsoniiなどの種が特定されました。
◆この研究は、バルトネラ菌が精神病の潜在的な原因である可能性を示しており、さらに研究を進める必要があるとしています。また、バルトネラ感染の抗体検査は精神病患者と対照群で有意な差がなかったことから、抗体検査だけでは不十分であることも示唆しています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ncsu.edu/2024/06/bartonella-dna-found-in-blood-of-patients-with-psychosis/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1388442/full
成人の精神病に関連するバルトネラ属菌血症
Bartonella species bacteremia in association with adult psychosis
Shannon Delaney,Cynthia Robveille,Ricardo G. Maggi,Erin Lashnits,Emily Kingston,Chance Liedig,Lilly Murray,Brian A. Fallon,Edward B. Breitschwerdt
Frontiers in Psychiatry Published:07 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1388442
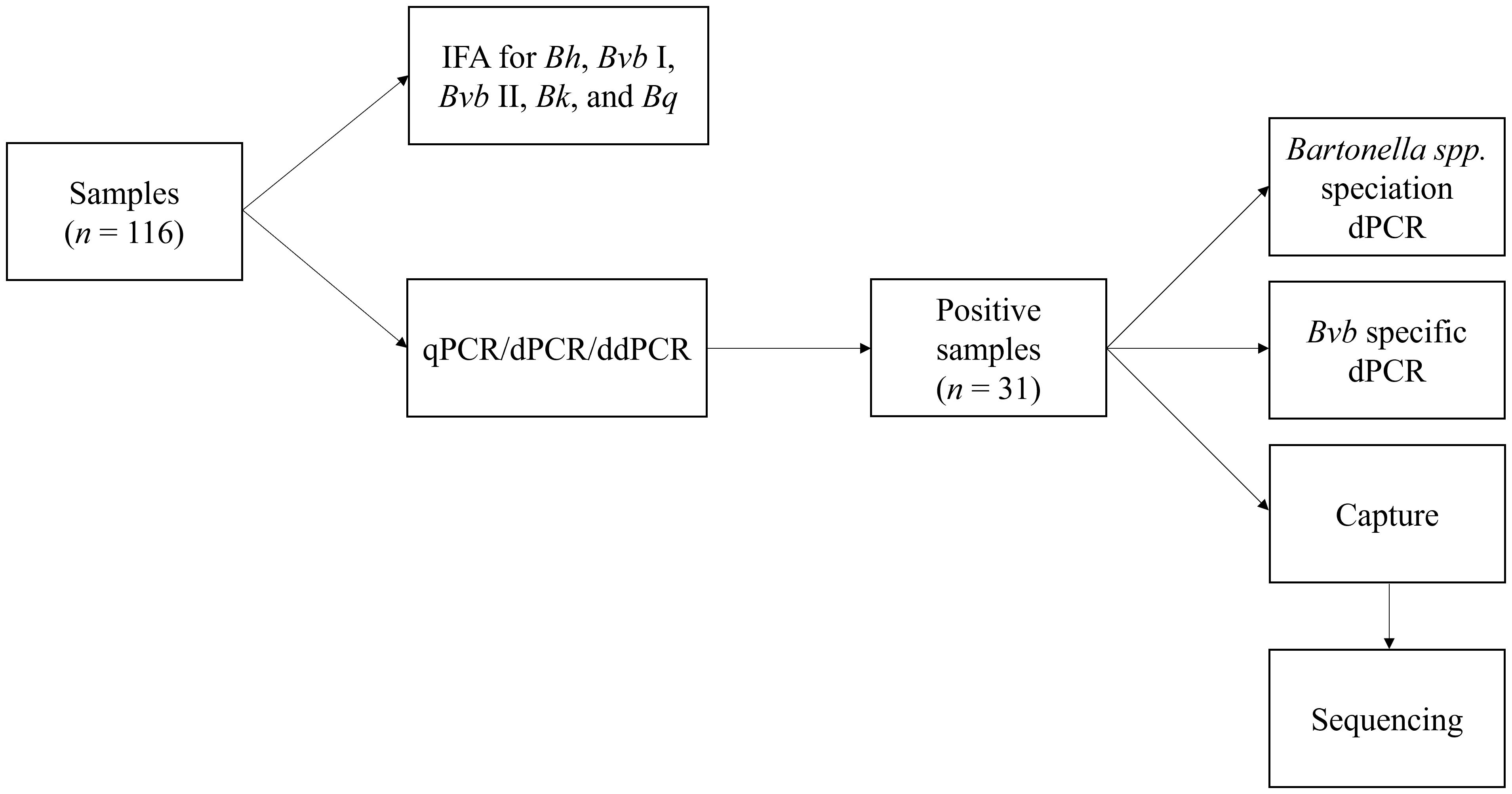
Introduction: The potential role of pathogens, particularly vector-transmitted infectious agents, as a cause of psychosis has not been intensively investigated. We have reported a potential link between Bartonella spp. bacteremia and neuropsychiatric symptoms, including pediatric acute onset neuropsychiatric syndrome and schizophrenia. The purpose of this study was to further assess whether Bartonella spp. exposure or infection are associated with psychosis.
Methods: In a blinded manner, we assessed the presence of anti-Bartonella antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence assays (IFA), and infection by amplification of bacterial DNA from blood by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), digital PCR (dPCR), and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) in 116 participants. Participants were categorized into one of five groups: 1) controls unaffected by psychosis (n = 29); 2) prodromal participants (n = 16); 3) children or adolescents with psychosis (n = 7); 4) adults with psychosis (n = 44); and 5) relatives of a participant with psychosis (n = 20).
Results: There was no significant difference in Bartonella spp. IFA seroreactivity between adults with psychosis and adult controls unaffected by psychosis. There was a higher proportion of adults with psychosis who had Bartonella spp. DNA in the bloodstream (43.2%) compared to adult controls unaffected by psychosis (14.3%, p = 0.021). The Bartonella species was determined for 18 of the 31 bacteremic participants, including infection or co-infection with Bartonella henselae (11/18), Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii (6/18), Bartonella quintana (2/18), Bartonella alsatica (1/18), and Bartonella rochalimae (1/18).
Discussion: In conjunction with other recent research, the results of this study provide justification for a large national or international multi-center study to determine if Bartonella spp. bacteremia is more prevalent in adults with psychosis compared to adults unaffected by psychosis. Expanding the investigation to include a range of vector-borne and other microbial infections with potential CNS effects would enhance knowledge on the relationship between psychosis and infection.


