2025-01-30 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
ルートヴィヒ・マクシミリアン大学ミュンヘン(LMU)の研究チームは、人工知能(AI)を活用して、がん治療の個別化を促進する新たな手法を開発しました。このアプローチでは、患者ごとの腫瘍特性や治療反応を詳細に分析するために、マルチオミクスデータ(ゲノム、トランスクリプトーム、プロテオームなど)をAIモデルに組み込みます。これにより、各患者に最適な治療法を予測し、治療効果を最大化することが可能となります。この研究は、AIとビッグデータを組み合わせることで、がん治療の精度と効果を向上させる可能性を示しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/artificial-intelligence-improves-personalized-cancer-treatment.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-024-00891-1
マルチモーダルな実世界データと説明可能な人工知能を用いて全癌の治療成績を解読するDecoding pan-cancer treatment outcomes using multimodal real-world data and explainable artificial intelligence
Julius Keyl,Philipp Keyl,Grégoire Montavon,René Hosch,Alexander Brehmer,Liliana Mochmann,Philipp Jurmeister,Gabriel Dernbach,Moon Kim,Sven Koitka,Sebastian Bauer,Nikolaos Bechrakis,Michael Forsting,Dagmar Führer-Sakel,Martin Glas,Viktor Grünwald,Boris Hadaschik,Johannes Haubold,Ken Herrmann,Stefan Kasper,Rainer Kimmig,Stephan Lang,Tienush Rassaf,Alexander Roesch,… Jens Kleesiek
Nature Cancer Published:30 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-024-00891-1
Abstract
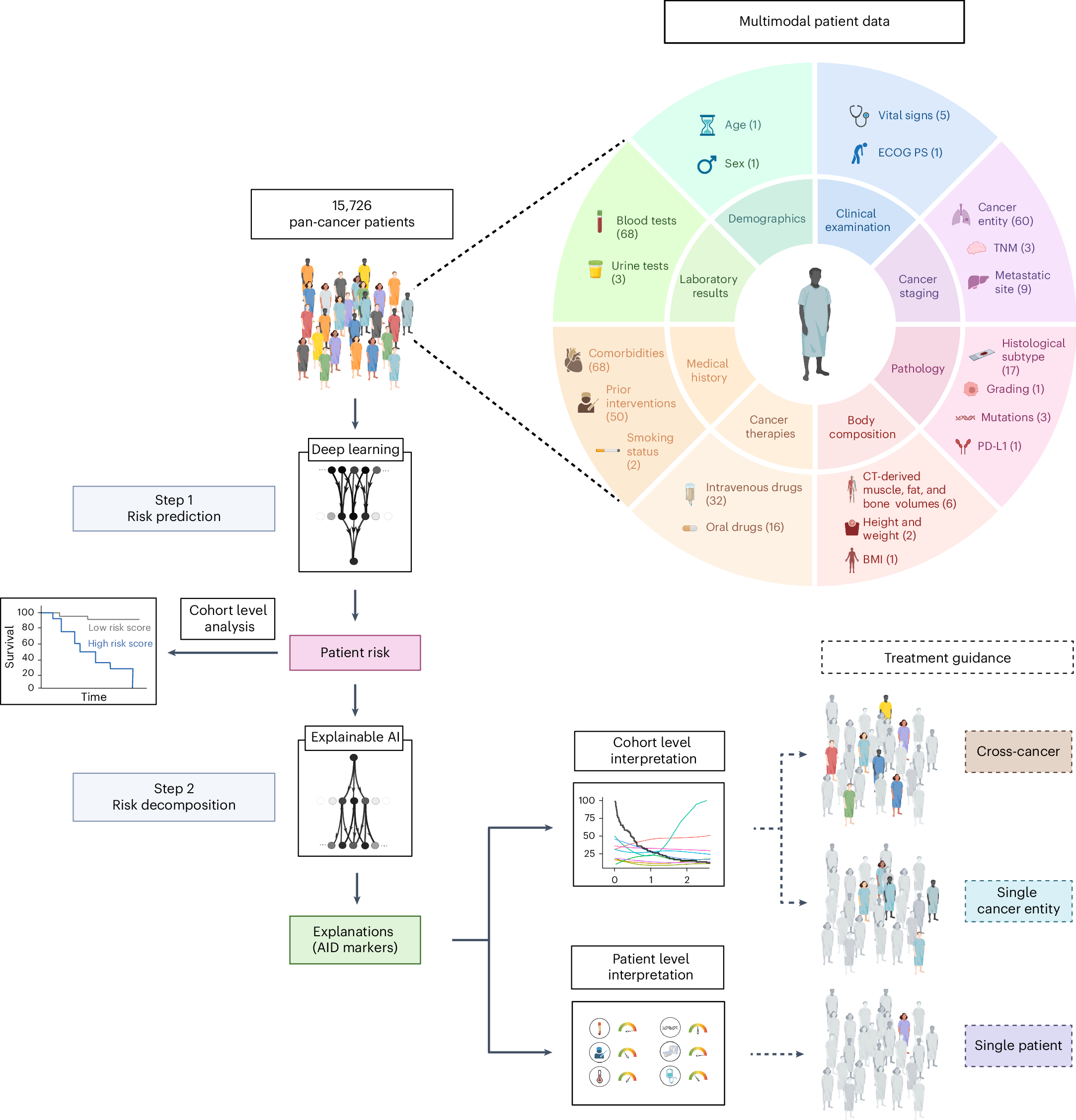
Despite advances in precision oncology, clinical decision-making still relies on limited variables and expert knowledge. To address this limitation, we combined multimodal real-world data and explainable artificial intelligence (xAI) to introduce AI-derived (AID) markers for clinical decision support. We used xAI to decode the outcome of 15,726 patients across 38 solid cancer entities based on 350 markers, including clinical records, image-derived body compositions, and mutational tumor profiles. xAI determined the prognostic contribution of each clinical marker at the patient level and identified 114 key markers that accounted for 90% of the neural network’s decision process. Moreover, xAI enabled us to uncover 1,373 prognostic interactions between markers. Our approach was validated in an independent cohort of 3,288 patients with lung cancer from a US nationwide electronic health record-derived database. These results show the potential of xAI to transform the assessment of clinical variables and enable personalized, data-driven cancer care.