2025-02-26 マサチューセッツ工科大学 (MIT)
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2025/tiny-tardigrades-protein-may-help-cancer-patients-tolerate-radiation-therapy-0226
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01360-5
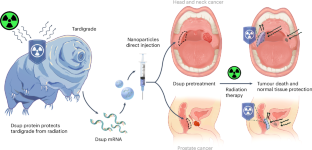
クマムシに見られる損傷抑制タンパク質をコードするmRNAをナノ粒子で送達することによる健康組織の放射線防護 Radioprotection of healthy tissue via nanoparticle-delivered mRNA encoding for a damage-suppressor protein found in tardigrades
Ameya R. Kirtane,Jianling Bi,Netra U. Rajesh,Chaoyang Tang,Miguel Jimenez,Emily Witt,Megan K. McGovern,Arielle B. Cafi,Samual J. Hatfield,Lauren Rosenstock,Sarah L. Becker,Nicole Machado,Veena Venkatachalam,Dylan Freitas,Xisha Huang,Alvin Chan,Aaron Lopes,Hyunjoon Kim,Nayoon Kim,Joy E. Collins,Michelle E. Howard,Srija Manchkanti,Theodore S. Hong,James D. Byrne & Giovanni Traverso
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published:26 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01360-5
Abstract
Patients undergoing radiation therapy experience debilitating side effects because of toxicity arising from radiation-induced DNA strand breaks in normal peritumoural cells. Here, inspired by the ability of tardigrades to resist extreme radiation through the expression of a damage-suppressor protein that binds to DNA and reduces strand breaks, we show that the local and transient expression of the protein can reduce radiation-induced DNA damage in oral and rectal epithelial tissues (which are commonly affected during radiotherapy for head-and-neck and prostate cancers, respectively). We used ionizable lipid nanoparticles supplemented with biodegradable cationic polymers to enhance the transfection efficiency and delivery of messenger RNA encoding the damage-suppressor protein into buccal and rectal tissues. In mice with orthotopic oral cancer, messenger RNA-based radioprotection of normal tissue preserved the efficacy of radiation therapy. The strategy may be broadly applicable to the protection of healthy tissue from DNA-damaging agents.

