2025-07-16 国立循環器病研究センター
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncvc.go.jp/pr/release/pr_48191/
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanwpc/article/PIIS2666-6065(25)00160-9/fulltext
21世紀日本の心血管疾患動向に対する心血管危険因子の寄与の定量化:マイクロシミュレーション研究 Quantifying the contributions of cardiovascular risk factors to cardiovascular disease trends in 21st century Japan: a microsimulation study
Soshiro Ogata ∙ Eri Kiyoshige ∙ Yusuke Yoshikawa ∙ Koji Iihara ∙ Hitoshi Fukuda ∙ Masanobu Ishii ∙ et al.
The Lancet Regional Health – Western Pacific Published: July 8, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2025.101623
Summary
Background
Recent stagnation or worsening trends in cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) and obesity, might slow the decline in Japan’s CVD burden. We aimed to quantify the impact of national changes in CVD risk factor distributions on Japan’s CVD burden from 2001 to 2019.
Methods
We conducted a microsimulation study with counterfactual analysis using IMPACTNCD-JPN, a validated model based on real-world data. It simulated a synthetic Japanese population (ages 30–99) from 2001 to 2019 using life-course data on seven CVD risk factors, estimating CVD incidence, mortality, and healthcare economics for synthetic individuals. The base-case reflected observed trends; counterfactual scenarios assumed 2001 levels persisted. Primary outcome was national CVD incidence (stroke and coronary heart disease).
Findings
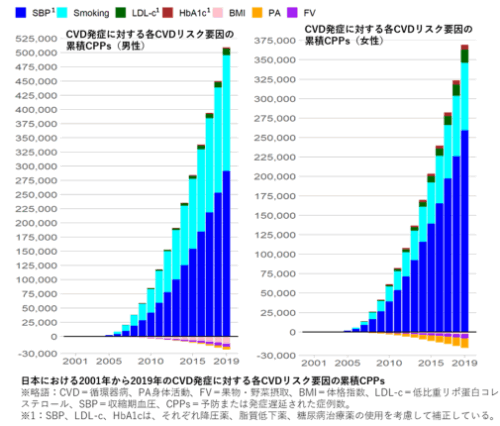
From 2001 to 2019, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and smoking declined markedly (men/women) by 6·8/7·2 mmHg and 18·4/6·8%, respectively, while LDL-c, HbA1c, body mass index (BMI), physical activity (PA), and fruit/vegetable (FV) consumption showed smaller or adverse trends. Under the base-case and counterfactual scenarios, IMPACTNCD-JPN estimated CVD incidence and quantified the differences between the scenarios. The changes in the CVD risk factors prevented or postponed 840,000 (95% uncertainty interval: 540,000–1,300,000) national CVD cases, cumulative from 2001 to 2019. Individual contributions were: SBP 540,000; smoking 280,000; LDL-c 27,000; HbA1c 7900; BMI -15,000; PA -16,000; and FV consumption -11,000.
Interpretation
SBP and smoking reductions drove most CVD burden declines in Japan (2001–2019). Modest benefits came from LDL-c and HbA1c, while rising BMI, and low PA and FV intake partly offset these benefits.
Funding
JSPS KAKENHIJP22K17821, JP25K02863; the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Comprehensive Research on Life-Style Related 22FA1015, 24FA1015.