2025-08-14 国立精神・神経医療研究センター
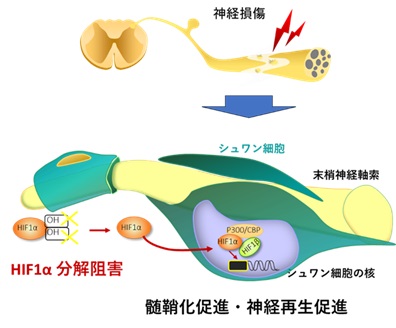
<模式図>末梢神経損傷後の再生過程におけるHIF1αの働き
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncnp.go.jp/topics/detail.php?@uid=ATmQRtp7zGzTtYqq
- https://www.ncnp.go.jp/press_search/images/files/NCNP%20PR_20250814.pdf
- https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(25)02283-5/fulltext
シュワン細胞における低酸素誘導因子1αが末梢神経のミエリン化を促進する Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in Schwann cells promotes peripheral nerve myelination
Yuka Kobayashi-Ujiie ∙ Shuji Wakatsuki ∙ … ∙ Yasuyuki Ohkawa ∙ Nobuhito Goda ∙ Toshiyuki Araki
Journal of Biological Chemistry Published:July 1, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110433
Abstract
Schwann cells are essential for supporting the metabolic activity of neurons and myelination in the peripheral nervous system. While hypoxia is known to influence development in aerobic organisms and has recently been shown to regulate oligodendrocyte differentiation in the central nervous system, its role in Schwann cell function remains less understood. Here we demonstrate that hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) in Schwann cells promotes peripheral nerve myelination. HIF1α protein expression is post-transcriptionally regulated and highly induced in myelinating Schwann cells during development and after injury. We also demonstrated that peripheral nerve tissue experiences hypoxic conditions during physiological development and during regeneration following injury. Stabilization or overexpression of HIF1α in Schwann cells promotes myelination in culture. Analysis of HIF1α targets revealed that HIF1α upregulates genes associated with Schwann cell myelination and repair. Furthermore, conditional deletion of HIF1α in Schwann cells results in delayed morphological and functional recovery from peripheral nerve injury. Together, these findings identify HIF1α as a novel regulator of Schwann cell myelination and nerve repair.