2025-09-30 京都大学
Web要約 の発言:
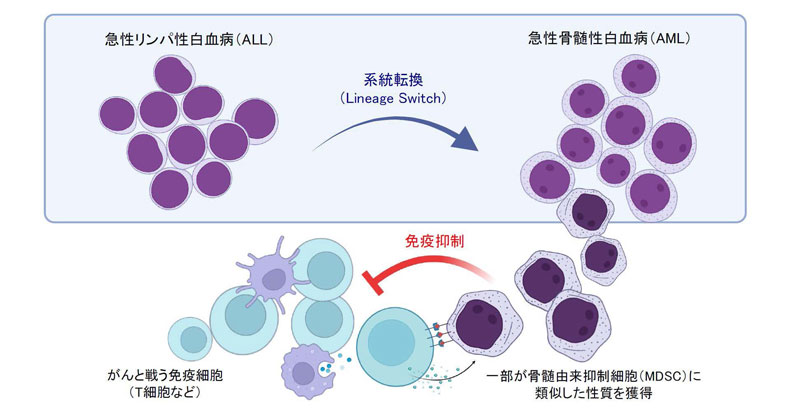
白血病の系統転換(Lineage Switch)とMDSC様分画による免疫抑制(上図はBioRenderで作成。作者:三上貴司(https://biorender.com/4xvinx3)、ライセンス: CC BY 4.0。)
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-09-30-0
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-09/web_250929_Mikami-6cb1b0bb49134925cb1e936e291c9073.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63271-y
マルチオミクス解析により、 KMT2A再構成を伴う系統スイッチAMLにおけるM-MDSC様免疫抑制表現型が同定された Multi-omics analysis identifies an M-MDSC-like immunosuppressive phenotype in lineage-switched AML with KMT2A rearrangement
Takashi Mikami,Itaru Kato,Akira Nishimura,Minenori Eguchi-Ishimae,Tatsuya Kamitori,Keiji Tasaka,Hirohito Kubota,Tomoya Isobe,Yoshinori Uchihara,Yui Namikawa,Satoru Hamada,Shinichi Tsujimoto,Shotaro Inoue,Takayuki Hamabata,Kazushi Izawa,Takako Miyamura,Daisuke Tomizawa,Toshihiko Imamura,Hidemi Toyoda,Mariko Eguchi,Hiroaki Goto,Seishi Ogawa,Masatoshi Takagi,James Badger Wing & Junko Takita
Nature Communications Published:26 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-63271-y
Abstract
Lineage switching (LS) is the conversion of cancer cell lineage during the course of a disease. LS in leukemia cell lineage facilitates cancer cells escaping targeting strategy like CD19 targeted immunotherapy. However, the genetic and biological mechanisms underlying immune evasion by LS leukemia cells are not well understood. Here, we conduct a multi-omics analysis of patient samples and find that lineage-switched acute myeloid leukemia (LS AML) cells with KMT2A rearrangement (KMT2A-r) possess monocytic myeloid derived suppressor cell (M-MDSC)-like characteristics. Single-cell mass cytometry analysis reveals an increase in the M-MDSC like LS AML as compared to those of lineage-consistent KMT2A-r AML, and single-cell transcriptomics identify distinct expression patterns of immunoregulatory genes within this population. Furthermore, in vitro assays confirm the immunosuppressive capacity of LS AML cells against T cells, which is analogous to that of MDSCs. These data provide insight into the immunological aspects of the complex pathogenesis of LS AML, as well as development of future treatments.