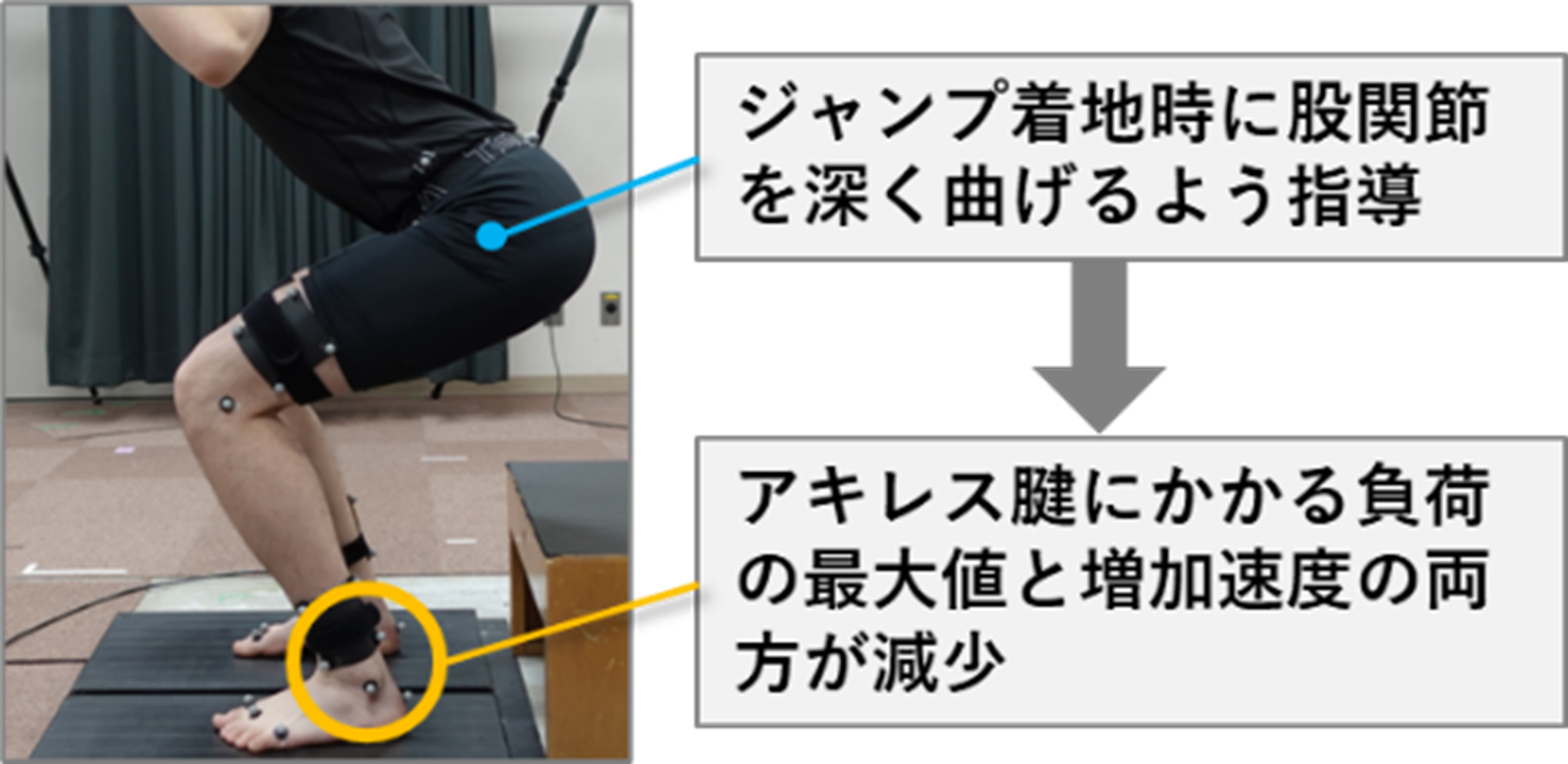
2025-10-09 中国科学院(CAS)
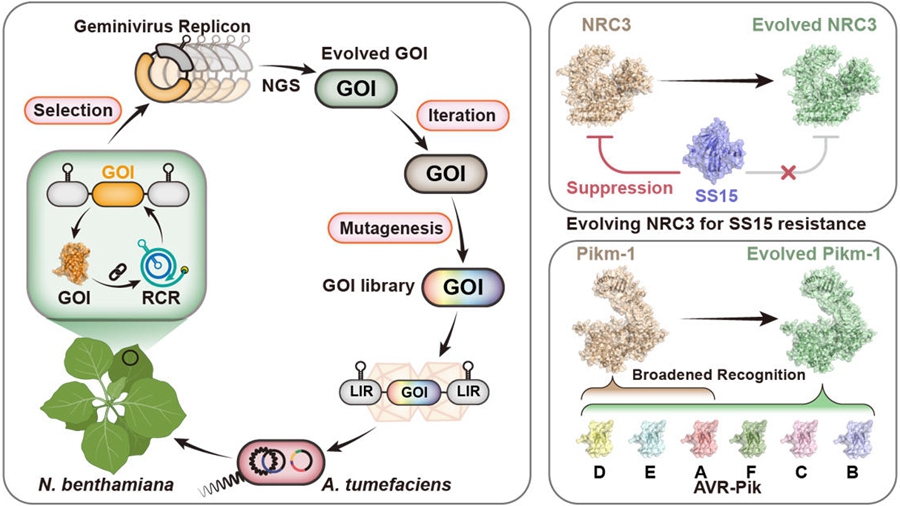
Graphical representation of GRAPE and its applications (Image by IGDB)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202510/t20251009_1075518.shtml
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ady2167
遺伝子操作されたジェミニウイルスレプリコンは植物体内での急速な進化を可能にする Engineered geminivirus replicons enable rapid in planta directed evolution
Haocheng Zhu, Xu Qin, Leyan Wei, Dandan Jiang, […] , and Caixia Gao
Science Published:2 Oct 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.ady2167
Abstract
Directed evolution can rapidly generate genetic variants with new and enhanced properties, yet efficient platforms for performing such evolution directly in plant cells have been lacking. We developed Geminivirus Replicon-Assisted in Planta Directed Evolution (GRAPE), a system that links gene function to geminivirus rolling circle replication (RCR) to enable high-throughput selection for desired activities. GRAPE supports the screening of up to 105 variants on a single Nicotiana benthamiana leaf within four days. Using GRAPE, we evolved the immune receptor NRC3 to resist inhibition by the nematode effector SPRYSEC15 and broadened the recognition spectrum of the rice immune receptor Pikm-1 to recognize all six alleles of the fungal effector AVR-Pik. GRAPE provides a rapid, scalable, and generalizable platform for directed evolution of diverse genes in plant cellular context.