2025-10-16 東京科学大学
Web要約 の発言:
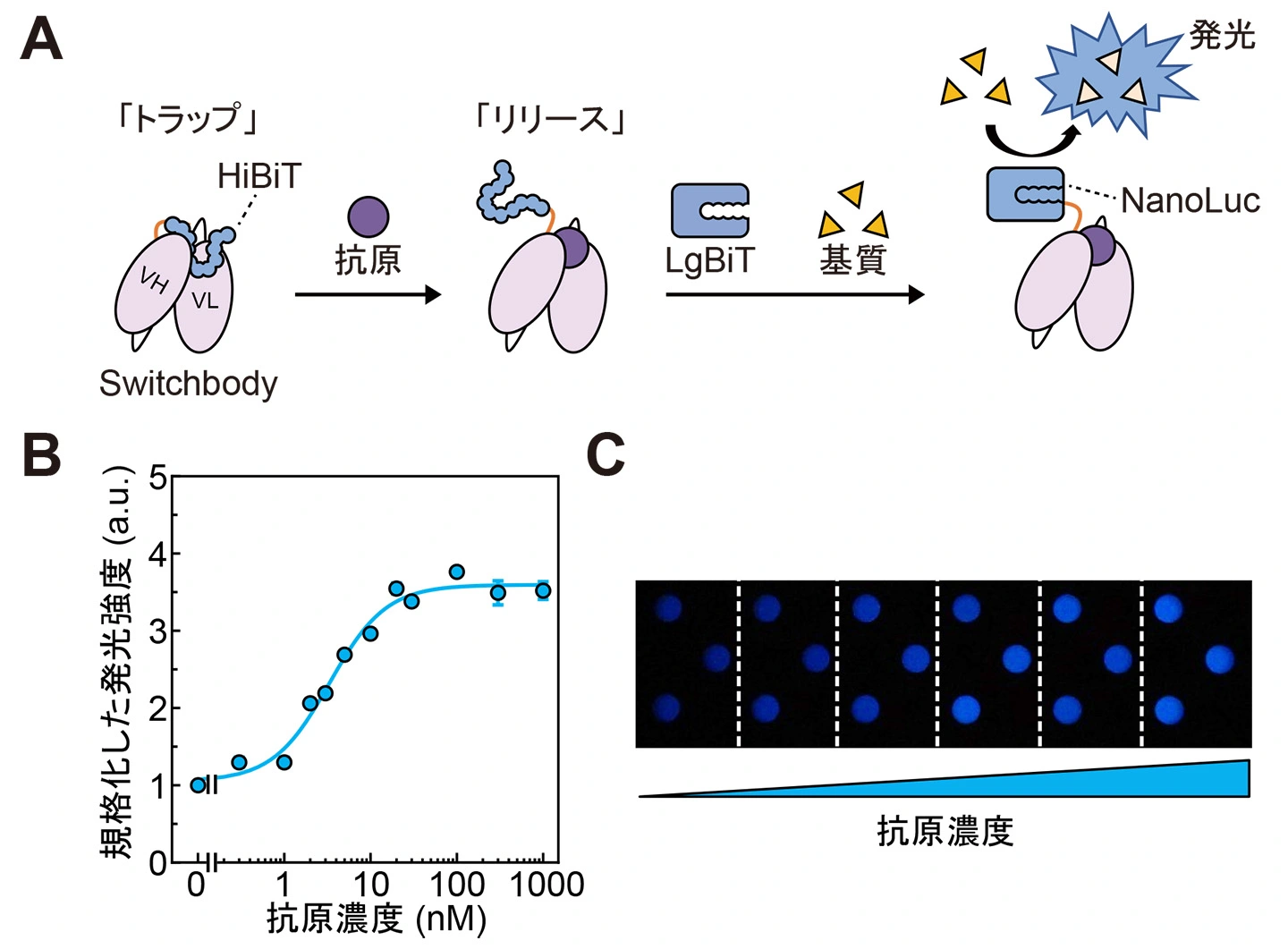
図1. (A)Switchbodyの模式図(B, C)抗原を添加したときのSwitchbodyの発光強度変化(DOI:10.1002/advs.202508422より一部改変)
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/ospry020twom
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2480&prevId=&key=12b25b485a438d4df1c929691652d7cc.pdf
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202508422
抗体に基づく抗原応答性酵素スイッチ「スイッチボディ」とその動作原理 Switchbody, an Antigen-Responsive Enzyme Switch Based on Antibody and Its Working Principle
Takanobu Yasuda, Yoshiyuki Ueno, Masahiko Taguchi, Naoya Tochio, Hiromasa Yagi, Shuma Yazaki, Ryoichi Arai, Bo Zhu, Takanori Kigawa, Hiroshi Ueda, Tetsuya Kitaguchi
Advances Science Published: 15 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202508422
Abstract
An enzyme switch, termed “Switchbody”, is developed by fusing an antibody with a fragment of a split enzyme for the precise regulation of enzyme activity in response to an antigen. A luciferase-based Switchbody is engineered by fusing the NanoLuc luciferase fragment HiBiT to the N-terminus of an antibody. The enzyme activity of the Switchbody increases upon the addition of an antigen in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of the complementary fragment LgBiT and its substrate furimazine, demonstrating the potential of the luciferase-based Switchbody as a biosensor. As its working principle, ELISA shows that the interaction between HiBiT and LgBiT is facilitated by antigen binding. Moreover, X-ray crystallography and NMR reveal the heterogeneous trapped state of the HiBiT region and an increasing motility of HiBiT region upon antigen binding, respectively. MD simulations and luminescence measurements show that antigen disrupted the trapping of HiBiT in the antibody, enabling its release. By applying this “Trap and Release” principle to Protein M, an antibody-binding protein, label-free IgG antibodies are successfully converted into bioluminescent Switchbodies. This adaptable Switchbody platform has the potential to expand switching technology beyond luciferase to various other enzymes in the future.