2025-10-27 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校 (EPFL)

MagFlow and OmniMag, guided by a stylus. 2025 EPFL/Alain Herzog CC BY SA
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/microcatheter-delivers-therapies-to-the-tiniest–2/
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.adu4003
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20195-z
超選択的動脈塞栓術のための血流駆動型磁気マイクロカテーテル Flow-driven magnetic microcatheter for superselective arterial embolization
Lucio Pancaldi, Ece Özelçi, Mehdi Ali Gadiri, Julian Raub, […] , and Mahmut Selman Sakar
Science Robotics Published:22 Oct 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.adu4003
Abstract
Minimally invasive interventions performed inside brain vessels with the synergistic use of microcatheters pushed over guidewires have revolutionized the way aneurysms, strokes, arteriovenous malformations, brain tumors, and other cerebrovascular conditions are being treated. However, a substantial portion of the brain vasculature remains inaccessible because the conventional catheterization technique based on transmitting forces from the proximal to the distal end of the instruments imposes stringent constraints on their diameter and stiffness. Here, we overcame this mechanical barrier by microengineering ultraminiaturized magnetic microcatheters in the form of an inflatable flat tube, making them ultraflexible and capable of harnessing the kinetic energy of blood flow for endovascular navigation. We introduce a compact and versatile magnetic steering platform that is compatible with conventional biplane fluoroscope imaging and demonstrate safe and effortless navigation and tracking of hard-to-reach, distal, tortuous arteries that are as small as 180 micrometers in diameter with a curvature radius as small as 0.69 millimeters. Furthermore, we demonstrate the superselective infusion of contrast and embolic liquid agents, all in a porcine model. These results pave the way to reach, diagnose, and treat currently inaccessible distal arteries that may be at risk of bleeding or feeding a tumor. Our endovascular technology can also be used to selectively target tissues for drug or gene delivery from within the arteries, not only in the central and peripheral nervous systems but also in almost any other organ system, with improved accuracy, speed, and safety.
マイクロエンジニアリングされた血管内プローブの流体駆動ロボットナビゲーション Flow driven robotic navigation of microengineered endovascular probes
Lucio Pancaldi,Pietro Dirix,Adele Fanelli,Augusto Martins Lima,Nikolaos Stergiopulos,Pascal John Mosimann,Diego Ghezzi & Mahmut Selman Sakar
Nature Communications Published:22 December 2020
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20195-z
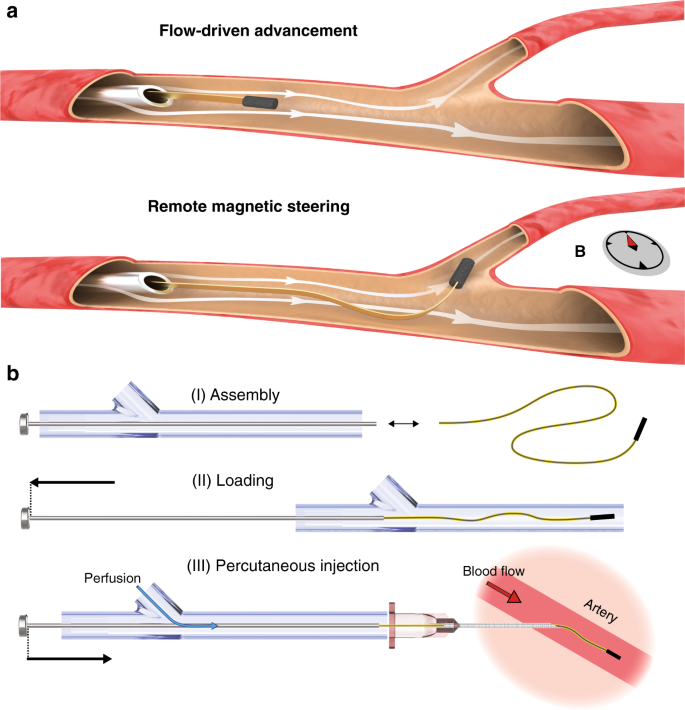
Abstract
Minimally invasive medical procedures, such as endovascular catheterization, have considerably reduced procedure time and associated complications. However, many regions inside the body, such as in the brain vasculature, still remain inaccessible due to the lack of appropriate guidance technologies. Here, experimentally and through numerical simulations, we show that tethered ultra-flexible endovascular microscopic probes can be transported through tortuous vascular networks with minimal external intervention by harnessing hydrokinetic energy. Dynamic steering at bifurcations is performed by deformation of the probe head using magnetic actuation. We developed an endovascular microrobotic toolkit with a cross-sectional area that is orders of magnitude smaller than the smallest catheter currently available. Our technology has the potential to improve state-of-the-art practices as it enhances the reachability, reduces the risk of iatrogenic damage, significantly increases the speed of robot-assisted interventions, and enables the deployment of multiple leads simultaneously through a standard needle injection and saline perfusion.


