2026-01-26 北海道大学
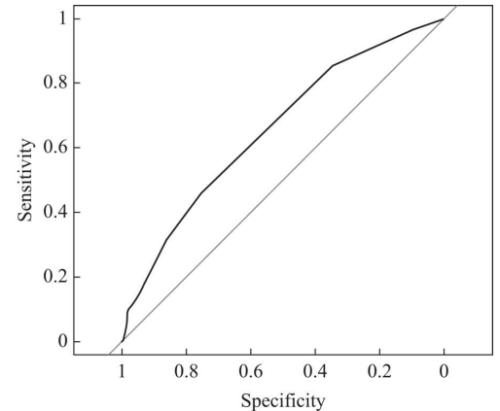
図 1. 当研究の予測モデルの性能を示す ROC 曲線。ROC:Receiver Operating Characteristic 曲線は診断モデルや予測モデルの性能を評価するための指標で、感度(見逃さない力)と特異度(誤認しない力)のバランスを視覚的に示す曲線。曲線が左上に近いほど、モデルの判別性能が高いことを示す。
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2026/01/post-2173.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/260126_pr.pdf
- https://www.journalofhospitalinfection.com/article/S0195-6701(25)00407-4/abstract
菌血症抗菌薬治療後早期臨床予測モデル Early prediction model for antibiotic treatment failure in bacteraemia: Japan bacteremia inpatient cohort association
H. Iwata ∙ M. Kaneko ∙ K. Kamada ∙ … ∙ S. Hamada ∙ T. Saito ∙ T. Aoki
Journal of Hospital Infection Published:December 1, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2025.11.031
Summary
Introduction
Early antibiotic treatment failure (EATF) is a clinically important concept but remains underrecognized among frontline physicians. Moreover, no validated prediction models currently exist that specifically target EATF in patients with bacteraemia. The present study aims to develop and internally validate a clinical prediction model for EATF in hospitalised adults with bacteraemia.
Methods
This multi-centre retrospective cohort study included adult inpatients with bacteremia from the Japan Bacteremia Inpatient Cohort Association, conducted across eight community hospitals in Japan from 2018 to 2022. Based on review results, we defined EATF as an outcome that included changes in antibiotics and advanced treatment after 72 h of admission. Using 28 candidate variables from previous studies, models and clinical expertise, we developed our model through backward elimination based on the Akaike Information Criterion. After constructing the score model, discrimination was assessed using the area under the curve (AUC), while calibration was evaluated using a plot. Internal validation used the bootstrap method to assess AUC and overfitting.
Findings
Among the 1084 eligible patients, 388 experienced EATF. The model included abnormal white blood cell count, low serum albumin, occlusive lesions, transfer admission and oxygen therapy. Internal validation demonstrated an AUC of 0.66, 95% confidence interval (0.62, 0.69) and a calibration slope of 1.01.
Conclusions
Although the model’s discrimination was modest, this study highlights the importance of EATF as a clinical outcome and demonstrates the inherent difficulty of developing predictive models for bacteraemia. External validation is warranted.

