2026-02-02 エディンバラ大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/new-map-reveals-cancer-mutation-effects
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02496-5
変異スキャンにより、がん原性CTNNB1変異がシグナル伝達に多様な影響を及ぼすことが明らかになった Mutational scanning reveals oncogenic CTNNB1 mutations have diverse effects on signaling
Anagha Krishna,Alison Meynert,Karamjit Singh Dolt,Martijn Kelder,Agavni Mesropian,Ailith Ewing,Conny Brouwers,Jill WC Claassens,Margot M. Linssen,Shahida Sheraz,Gillian CA Taylor,Philippe Gautier,Anna Ferrer-Vaquer,Graeme Grimes,Hannes Becher,Ryan Silk,Albert Gris-Oliver,Roser Pinyol,Colin A. Semple,Timothy J. Kendall,Thomas Graham Bird,Anna-Katerina Hadjantonakis,Joseph A. Marsh,Josep M. Llovet,… Derya D. Ozdemir
Nature Genetics Published:02 February 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-025-02496-5
Abstract
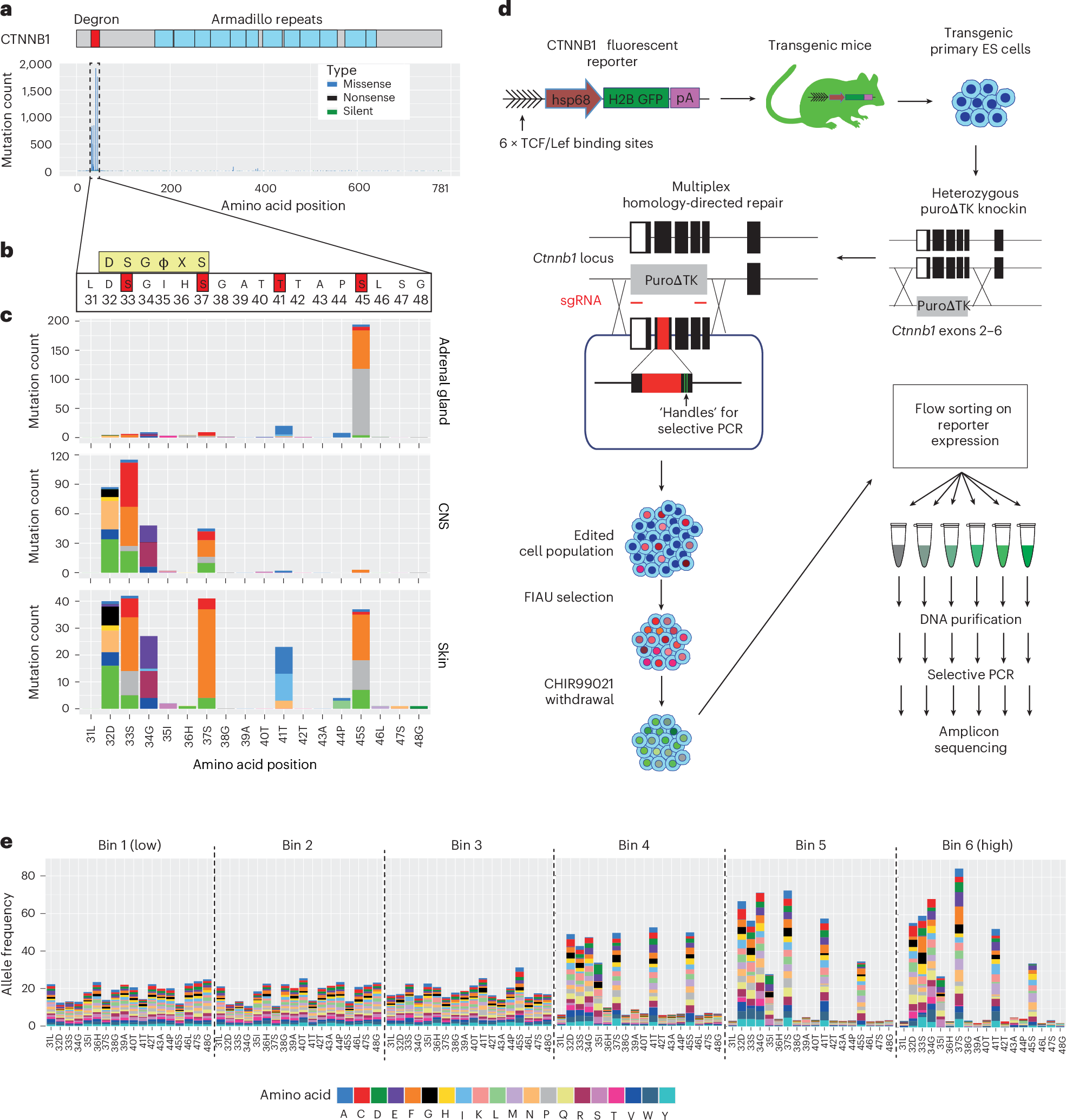
CTNNB1, the gene encoding β-catenin, is a frequent target for oncogenic mutations activating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, typically through missense mutations within a degron hotspot motif in exon 3. Here, we combine saturation genome editing with a fluorescent reporter assay to quantify signaling phenotypes for all 342 possible missense mutations in the mutation hotspot. Our data define the genetic requirements for β-catenin degron function, refine the consensus motif for substrate recognition by β-TRCP and reveal diverse levels of signal activation among known driver mutations. Tumorigenesis in different human tissues involves selection for CTNNB1 mutations spanning distinct ranges of predicted activity. In hepatocellular carcinoma, mutation effect scores distinguish two tumor subclasses with different levels of β-catenin signaling, and weaker mutations predict greater immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. Our work provides a resource to understand mutational diversity within a pan-cancer mutation hotspot, with potential implications for targeted therapy.