2022-04-14 大韓民国・基礎科学研究院(IBS)
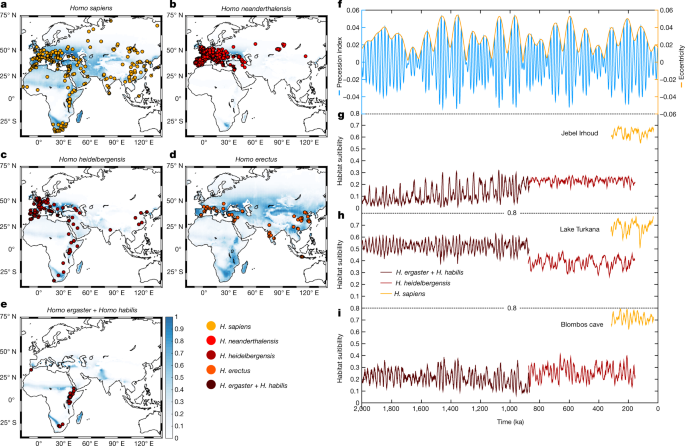
・気候モデル、人類学、生態学の専門家からなる研究チームは、化石や考古学的遺物の広範なデータベースと、過去200万年間の地球の気候史のシミュレーションと組み合わせることにより、旧人類がどのような環境条件のもとで暮らしていたかを明らかにした。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=21200&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04600-9
旧人類の生息地と種の継承における気候の影響 Climate effects on archaic human habitats and species successions
Axel Timmermann,Kyung-Sook Yun,Pasquale Raia,Jiaoyang Ruan,Alessandro Mondanaro,Elke Zeller,Christoph Zollikofer,Marcia Ponce de León,Danielle Lemmon,Matteo Willeit &Andrey Ganopolski
Nature Published: 13 April 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04600-9
Abstract
It has long been believed that climate shifts during the last 2 million years had a pivotal role in the evolution of our genus Homo1,2,3. However, given the limited number of representative palaeo-climate datasets from regions of anthropological interest, it has remained challenging to quantify this linkage. Here, we use an unprecedented transient Pleistocene coupled general circulation model simulation in combination with an extensive compilation of fossil and archaeological records to study the spatiotemporal habitat suitability for five hominin species over the past 2 million years. We show that astronomically forced changes in temperature, rainfall and terrestrial net primary production had a major impact on the observed distributions of these species. During the Early Pleistocene, hominins settled primarily in environments with weak orbital-scale climate variability. This behaviour changed substantially after the mid-Pleistocene transition, when archaic humans became global wanderers who adapted to a wide range of spatial climatic gradients. Analysis of the simulated hominin habitat overlap from approximately 300–400 thousand years ago further suggests that antiphased climate disruptions in southern Africa and Eurasia contributed to the evolutionary transformation of Homo heidelbergensis populations into Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, respectively. Our robust numerical simulations of climate-induced habitat changes provide a framework to test hypotheses on our human origin.