2023-05-24 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
◆この研究により、植物の根の成長を制御する新しい方法や、植物のストレス耐性を向上させるための化学物質や遺伝子戦略の開発に役立つ情報が得られました。
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/groundbreaking-images-of-root-chemicals-offer-new-insights-on-plant-growth
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-38150-z
ケミカルイメージングにより、トリカルボン酸代謝物の根の成長・発達における多様な機能を解明 Chemical imaging reveals diverse functions of tricarboxylic acid metabolites in root growth and development
Tao Zhang,Sarah E. Noll,Jesus T. Peng,Amman Klair,Abigail Tripka,Nathan Stutzman,Casey Cheng,Richard N. Zare & Alexandra J. Dickinson
Nature Communications Published:04 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38150-z
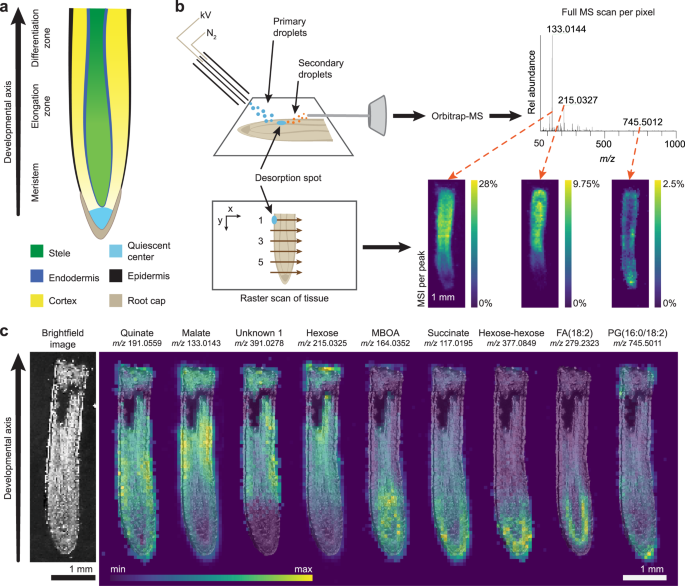
Abstract
Understanding how plants grow is critical for agriculture and fundamental for illuminating principles of multicellular development. Here, we apply desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging (DESI-MSI) to the chemical mapping of the developing maize root. This technique reveals a range of small molecule distribution patterns across the gradient of stem cell differentiation in the root. To understand the developmental logic of these patterns, we examine tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle metabolites. In both Arabidopsis and maize, we find evidence that elements of the TCA cycle are enriched in developmentally opposing regions. We find that these metabolites, particularly succinate, aconitate, citrate, and α-ketoglutarate, control root development in diverse and distinct ways. Critically, the developmental effects of certain TCA metabolites on stem cell behavior do not correlate with changes in ATP production. These results present insights into development and suggest practical means for controlling plant growth.


