2023-07-20 マックス・プランク研究所
◆この方法は、58箇所の異なる目標部位を変更することで効果を示し、ヒトの病気の治療にも応用の可能性がある。科学者たちはまた、貧血、鎌状赤血球症、血栓症の3つの遺伝病に苦しむ患者に由来する細胞の病原性変異を修正しました。しかし、患者への実用化にはまだ時間がかかるとの指摘もある。
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/20644398/0720-evan-dna-editing-new-method-150495-x
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-023-01949-1
HDRobustによる高精度相同性修復依存ゲノム編集の効率化 Efficient high-precision homology-directed repair-dependent genome editing by HDRobust
Stephan Riesenberg,Philipp Kanis,Dominik Macak,Damian Wollny,Dorothee Düsterhöft,Johannes Kowalewski,Nelly Helmbrecht,Tomislav Maricic & Svante Pääbo
Nature Methods Published:20 July 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-023-01949-1
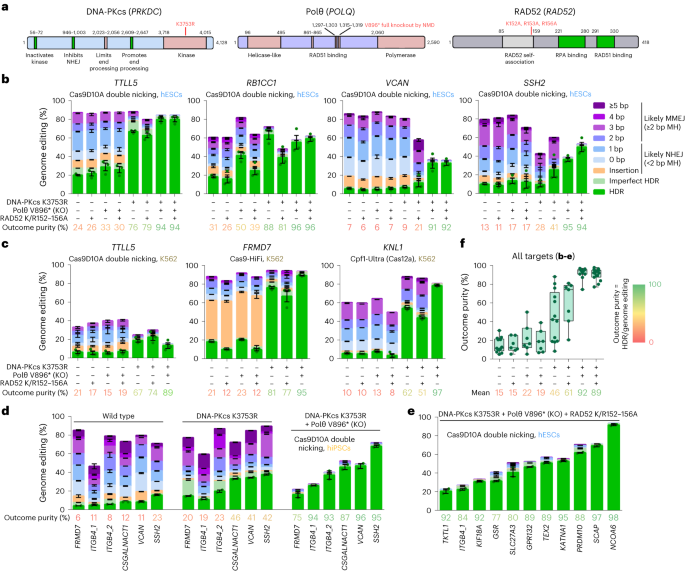
Abstract
Homology-directed repair (HDR), a method for repair of DNA double-stranded breaks can be leveraged for the precise introduction of mutations supplied by synthetic DNA donors, but remains limited by low efficiency and off-target effects. In this study, we report HDRobust, a high-precision method that, via the combined transient inhibition of nonhomologous end joining and microhomology-mediated end joining, resulted in the induction of point mutations by HDR in up to 93% (median 60%, s.e.m. 3) of chromosomes in populations of cells. We found that, using this method, insertions, deletions and rearrangements at the target site, as well as unintended changes at other genomic sites, were largely abolished. We validated this approach for 58 different target sites and showed that it allows efficient correction of pathogenic mutations in cells derived from patients suffering from anemia, sickle cell disease and thrombophilia.


