2024-02-22 インペリアル・カレッジ・ロンドン(ICL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/251593/virtual-biopsy-uses-ai-help-doctors/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41698-024-00502-3
組織メタボロームとコンピュータ断層撮影の深い表現学習がNSCLCの分類と予後に注釈を付ける Deep representation learning of tissue metabolome and computed tomography annotates NSCLC classification and prognosis
Marc Boubnovski Martell,Kristofer Linton-Reid,Sumeet Hindocha,Mitchell Chen,Paula Moreno,Marina Álvarez‐Benito,Ángel Salvatierra,Richard Lee,Joram M. Posma,Marco A. Calzado & Eric O. Aboagye
npj Precision Oncology Published:03 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-024-00502-3
Abstract
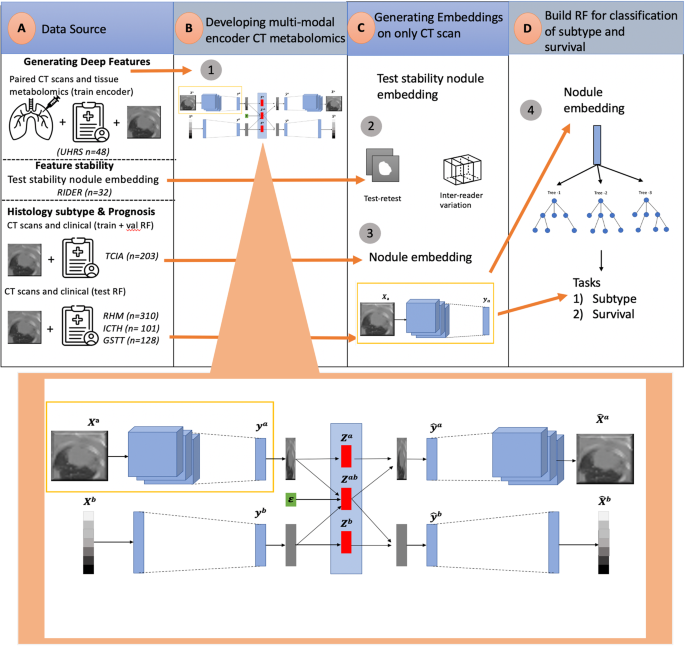
The rich chemical information from tissue metabolomics provides a powerful means to elaborate tissue physiology or tumor characteristics at cellular and tumor microenvironment levels. However, the process of obtaining such information requires invasive biopsies, is costly, and can delay clinical patient management. Conversely, computed tomography (CT) is a clinical standard of care but does not intuitively harbor histological or prognostic information. Furthermore, the ability to embed metabolome information into CT to subsequently use the learned representation for classification or prognosis has yet to be described. This study develops a deep learning-based framework — tissue-metabolomic-radiomic-CT (TMR-CT) by combining 48 paired CT images and tumor/normal tissue metabolite intensities to generate ten image embeddings to infer metabolite-derived representation from CT alone. In clinical NSCLC settings, we ascertain whether TMR-CT results in an enhanced feature generation model solving histology classification/prognosis tasks in an unseen international CT dataset of 742 patients. TMR-CT non-invasively determines histological classes – adenocarcinoma/squamous cell carcinoma with an F1-score = 0.78 and further asserts patients’ prognosis with a c-index = 0.72, surpassing the performance of radiomics models and deep learning on single modality CT feature extraction. Additionally, our work shows the potential to generate informative biology-inspired CT-led features to explore connections between hard-to-obtain tissue metabolic profiles and routine lesion-derived image data.