2024-05-21 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/signatures-of-heart-attack.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-02953-4
マルチオミクス解析により急性冠症候群と慢性冠症候群における免疫学的シグネチャーが明らかになった Multiomic analyses uncover immunological signatures in acute and chronic coronary syndromes
Kami Pekayvaz,Corinna Losert,Viktoria Knottenberg,Christoph Gold,Irene V. van Blokland,Roy Oelen,Hilde E. Groot,Jan Walter Benjamins,Sophia Brambs,Rainer Kaiser,Adrian Gottschlich,Gordon Victor Hoffmann,Luke Eivers,Alejandro Martinez-Navarro,Nils Bruns,Susanne Stiller,Sezer Akgöl,Keyang Yue,Vivien Polewka,Raphael Escaig,Markus Joppich,Aleksandar Janjic,Oliver Popp,Sebastian Kobold,… Konstantin Stark
Nature Medicine Published:21 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-02953-4
Abstract
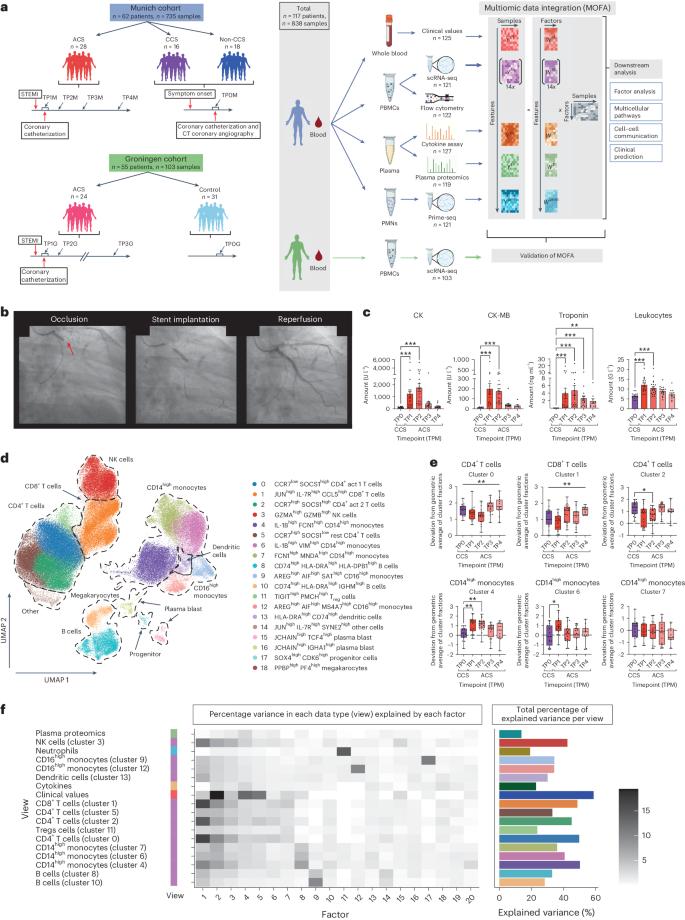
Acute and chronic coronary syndromes (ACS and CCS) are leading causes of mortality. Inflammation is considered a key pathogenic driver of these diseases, but the underlying immune states and their clinical implications remain poorly understood. Multiomic factor analysis (MOFA) allows unsupervised data exploration across multiple data types, identifying major axes of variation and associating these with underlying molecular processes. We hypothesized that applying MOFA to multiomic data obtained from blood might uncover hidden sources of variance and provide pathophysiological insights linked to clinical needs. Here we compile a longitudinal multiomic dataset of the systemic immune landscape in both ACS and CCS (n = 62 patients in total, n = 15 women and n = 47 men) and validate this in an external cohort (n = 55 patients in total, n = 11 women and n = 44 men). MOFA reveals multicellular immune signatures characterized by distinct monocyte, natural killer and T cell substates and immune-communication pathways that explain a large proportion of inter-patient variance. We also identify specific factors that reflect disease state or associate with treatment outcome in ACS as measured using left ventricular ejection fraction. Hence, this study provides proof-of-concept evidence for the ability of MOFA to uncover multicellular immune programs in cardiovascular disease, opening new directions for mechanistic, biomarker and therapeutic studies.