2024-06-18 ロイヤルメルボルン工科大学(RMIT)

<関連情報>
- https://www.rmit.edu.au/news/all-news/2024/june/stroke-face-screening
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0169260724001913?via%3Dihub
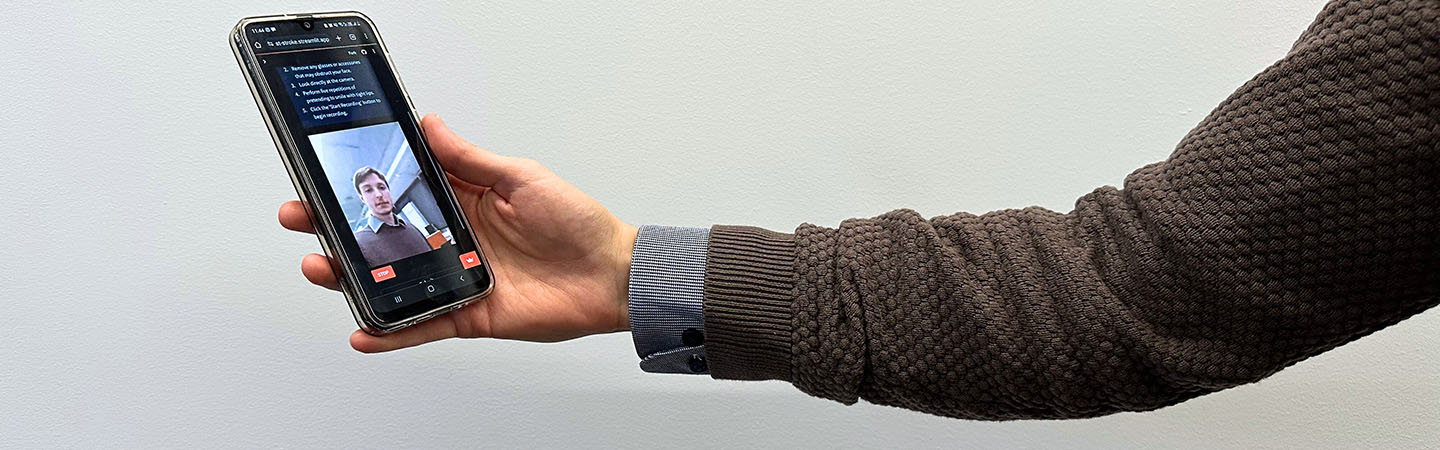
脳卒中後遺症を表情で判別 パイロット研究 Facial expressions to identify post-stroke: A pilot study
Guilherme C. Oliveira, Quoc C. Ngo, Leandro A. Passos, Leonardo S. Oliveira, João P. Papa, Dinesh Kumar
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Available online: 24 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108195
Highlights
- Computerized method to distinguish post-stroke patients using RGB videos.
- Kiss and Spread best differentiate post-stroke from others.
- This method is suitable for being used as a smartphone app.
Abstract
Background and Objective:
Timely stroke treatment can limit brain damage and improve outcomes, which depends on early recognition of the symptoms. However, stroke cases are often missed by the first respondent paramedics. One of the earliest external symptoms of stroke is based on facial expressions.
Methods:
We propose a computerized analysis of facial expressions using action units to distinguish between Post-Stroke and healthy people. Action units enable analysis of subtle and specific facial movements and are interpretable to the facial expressions. The RGB videos from the Toronto Neuroface Dataset, which were recorded during standard orofacial examinations of 14 people with post-stroke (PS) and 11 healthy controls (HC) were used in this study. Action units were computed using XGBoost which was trained using HC, and classified using regression analysis for each of the nine facial expressions. The analysis was performed without manual intervention.
Results:
The results were evaluated using leave-one-our validation. The accuracy was 82% for Kiss and Spread, with the best sensitivity of 91% in the differentiation of PS and HC. The features corresponding to mouth muscles were most suitable.
Conclusions:
This pilot study has shown that our method can detect PS based on two simple facial expressions. However, this needs to be tested in real-world conditions, with people of different ethnicities and smartphone use. The method has the potential for a computerized assessment of the videos for use by the first respondents using a smartphone to perform screening tests, which can facilitate the timely start of the treatment.