2025-03-05 東京大学,東海大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp/research/news/2025/20250305.html
- https://www.aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp/research/news/2025/files/20250305_summary.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-91208-4
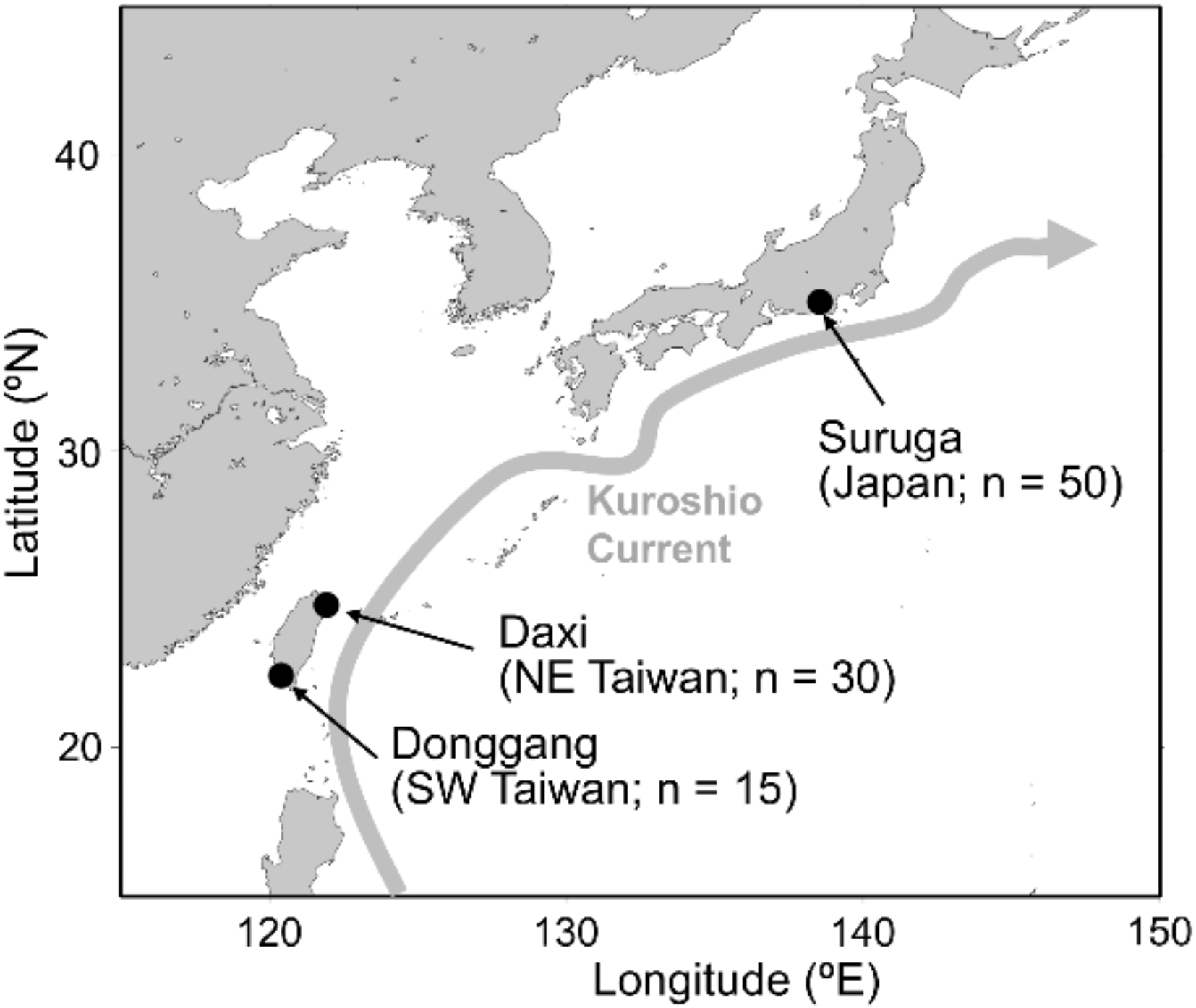
北太平洋西部における日本海域と台湾海域の外洋性エビLucensosergia lucensの個体群汎混合性 Population panmixia of the pelagic shrimp Lucensosergia lucens between Japanese and Taiwanese waters in the western North Pacific
Junya Hirai,Sheng-Tai Hsiao,Hsin-Ming Yeh & Jun Nishikawa
Scientific Reports Published:05 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-91208-4
Abstract
The pelagic shrimp Lucensosergia lucens is a commercially important species in Japan and Taiwan; however, a recent significant decline in L. lucens catch has been reported in Suruga Bay, Japan. In the present study, multiple molecular approaches were used to understand the population structure of L. lucens in Japanese and Taiwanese waters. Our analysis of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I and control region obtained by Sanger sequencing showed no evidence of different population structures, contrary to the previous study based on the control region. Genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis using multiplexed inter-simple sequence repeats genotyping by sequencing revealed panmixia in Japanese and Taiwanese populations. The contemporary migration rates estimated from the SNP data suggest that the Kuroshio Current plays a key role in L. lucens transportation from Taiwan to Japan. Additionally, mitogenome sequences obtained by genome skimming showed no region-specific genetic lineages in Japan or Taiwan. The results obtained by multiple molecular approaches suggested that L. lucens is widely distributed with a dispersal capacity in the Kuroshio and adjacent regions in the western North Pacific. Because apparent panmixia of L. lucens was observed in Japanese and Taiwanese waters, international cooperation is needed for the sustainable fishing of this shrimp.