2025-04-10 シンガポール国立大学(NUS)
<関連情報>
- https://news.nus.edu.sg/combating-lenalidomide-resistance-in-multiple-myeloma/
- https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/145/11/1164/534401/The-ADAR1-regulated-cytoplasmic-dsRNA-sensing
ADAR1が制御する細胞質dsRNA感知経路は、多発性骨髄腫におけるレナリドミド耐性の新規メカニズムである The ADAR1-regulated cytoplasmic dsRNA-sensing pathway is a novel mechanism of lenalidomide resistance in multiple myeloma
Mun Yee Koh,Tae-Hoon Chung,Nicole Xin Ning Tang,Sabrina Hui Min Toh,Jianbiao Zhou,Tze King Tan,Leilei Chen,Wee Joo Chng,Phaik Ju Teoh
blood Published:March 13, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2024024429
Key Points
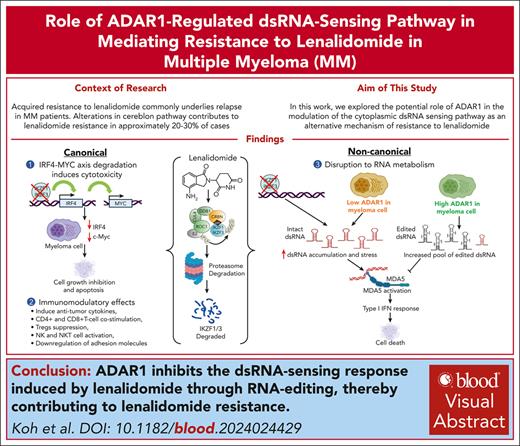
- Lenalidomide induces immunomodulating responses through the activation of dsRNA-sensing pathway.
- ADAR1 drives lenalidomide resistance in MM via the suppression of lenalidomide-induced dsRNA-sensingresponse.
Visual Abstract
Abstract
Immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) are a major class of drugs for treating multiple myeloma (MM); however, acquired resistance to IMiDs remains a significant clinical challenge. Although alterations in cereblon and its pathway are known to contribute to IMiD resistance, they account for only 20% to 30% of cases, and the underlying mechanisms in the majority of the resistance cases remain unclear. Here, we identified adenosine deaminase acting on RNA1 (ADAR1) as a novel driver of lenalidomide resistance in MM. We showed that lenalidomide activates the MDA5-mediated double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)–sensing pathway in MM cells, leading to interferon (IFN)-mediated apoptosis, with ADAR1 as the key regulator. Mechanistically, ADAR1 loss increased lenalidomide sensitivity through endogenous dsRNA accumulation, which in turn triggered dsRNA-sensing pathways and enhanced IFN responses. Conversely, ADAR1 overexpression reduced lenalidomide sensitivity, attributed to increased RNA editing frequency, reduced dsRNA accumulation, and suppression of the dsRNA-sensing pathways. In summary, we report the involvement of ADAR1-regulated dsRNA sensing in modulating lenalidomide sensitivity in MM. These findings highlight a novel RNA-related mechanism underlying lenalidomide resistance and underscore the potential of targeting ADAR1 as a novel therapeutic strategy.