2025-04-21 理化学研究所,島根大学,順天堂大学,静岡県立総合病院,静岡県立大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.riken.jp/press/2025/20250421_1/index.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08771-z
1,962,069人における変形性関節症のトランスレーショナルゲノミクス Translational genomics of osteoarthritis in 1,962,069 individuals
Konstantinos Hatzikotoulas,Lorraine Southam,Lilja Stefansdottir,Cindy G. Boer,Merry-Lynn McDonald,J. Patrick Pett,Young-Chan Park,Margo Tuerlings,Rick Mulders,Andrei Barysenka,Ana Luiza Arruda,Vinicius Tragante,Alison Rocco,Norbert Bittner,Shibo Chen,Susanne Horn,Vinodh Srinivasasainagendra,Ken To,Georgia Katsoula,Peter Kreitmaier,Amabel M. M. Tenghe,Arthur Gilly,Liubov Arbeeva,Lane G. Chen,arcOGEN Consortium,ARGO Consortium,DBDS Genomic Consortium,Estonian Biobank Research Team,FinnGen,Genes & Health Research Team,HUNT All-In Pain,Million Veteran Program,Regeneron Genetics Center,… Eleftheria Zeggini
Nature Published:09 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08771-z
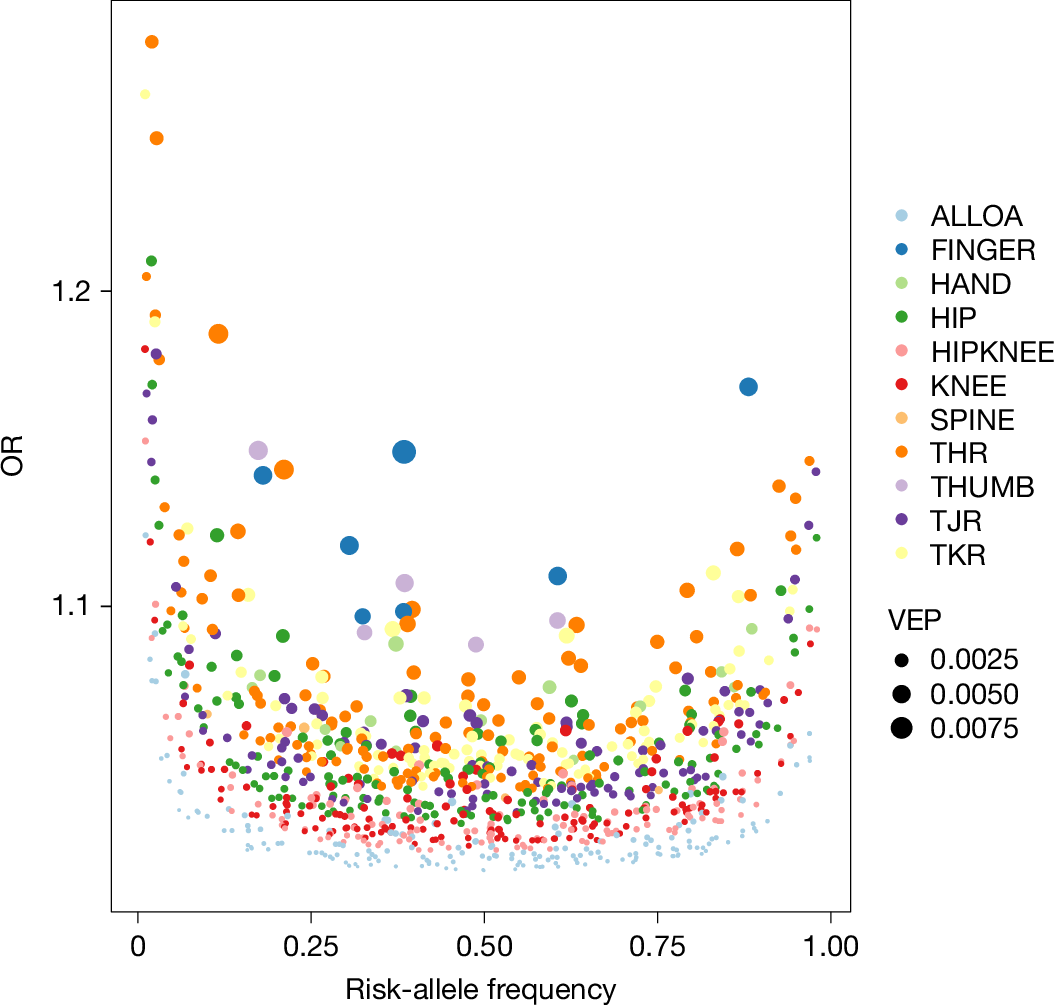
Abstract
Osteoarthritis is the third most rapidly growing health condition associated with disability, after dementia and diabetes1. By 2050, the total number of patients with osteoarthritis is estimated to reach 1 billion worldwide2. As no disease-modifying treatments exist for osteoarthritis, a better understanding of disease aetiopathology is urgently needed. Here we perform a genome-wide association study meta-analyses across up to 489,975 cases and 1,472,094 controls, establishing 962 independent associations, 513 of which have not been previously reported. Using single-cell multiomics data, we identify signal enrichment in embryonic skeletal development pathways. We integrate orthogonal lines of evidence, including transcriptome, proteome and epigenome profiles of primary joint tissues, and implicate 700 effector genes. Within these, we find rare coding-variant burden associations with effect sizes that are consistently higher than common frequency variant associations. We highlight eight biological processes in which we find convergent involvement of multiple effector genes, including the circadian clock, glial-cell-related processes and pathways with an established role in osteoarthritis (TGFβ, FGF, WNT, BMP and retinoic acid signalling, and extracellular matrix organization). We find that 10% of the effector genes express a protein that is the target of approved drugs, offering repurposing opportunities, which can accelerate translation.


