2025-04-23 東京科学大学
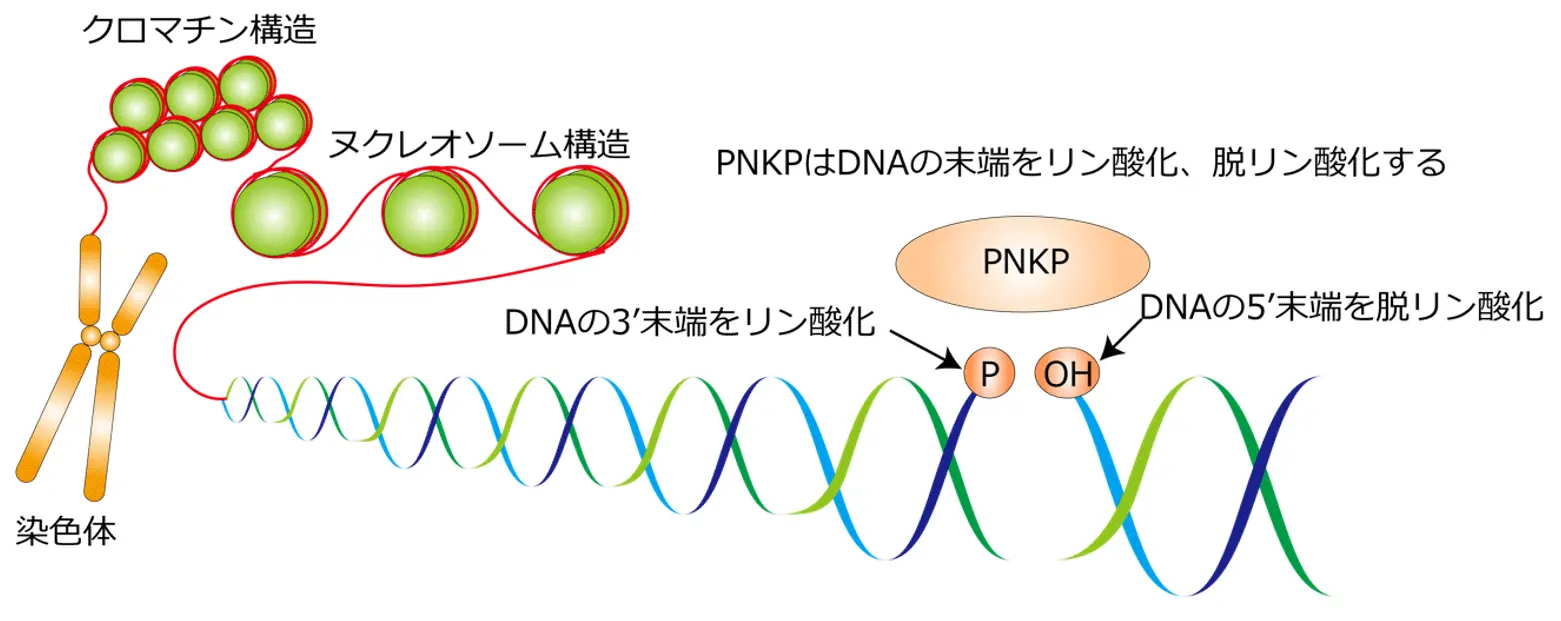 図1. PNKPはDNA修復に重要な酵素であり、DNA末端を直接、リン酸化あるいは脱リン酸化することによりDNA修復を円滑に進行させる機能を持つ。
図1. PNKPはDNA修復に重要な酵素であり、DNA末端を直接、リン酸化あるいは脱リン酸化することによりDNA修復を円滑に進行させる機能を持つ。
<関連情報>
CDKを介したPNKPのリン酸化は、岡崎フラグメント上の一本鎖DNAギャップの終末処理とゲノムの安定性に必要である CDK-mediated phosphorylation of PNKP is required for end-processing of single-strand DNA gaps on Okazaki fragments and genome stability
Kaima Tsukada ,Rikiya Imamura,Tomoko Miyake,Kotaro Saikawa,Mizuki Saito,Naoya Kase,Lingyan Fu,Masamichi Ishiai,Yoshihisa Matsumoto,Mikio Shimada
eLife Published:Mar 27, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.99217
Abstract
Polynucleotide kinase phosphatase (PNKP) has enzymatic activities as 3′-phosphatase and 5′-kinase of DNA ends to promote DNA ligation and repair. Here, we show that cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) regulate the phosphorylation of threonine 118 (T118) in PNKP. This phosphorylation allows recruitment to the gapped DNA structure found in single-strand DNA (ssDNA) nicks and/or gaps between Okazaki fragments (OFs) during DNA replication. T118A (alanine)-substituted PNKP-expressing cells exhibited an accumulation of ssDNA gaps in S phase and accelerated replication fork progression. Furthermore, PNKP is involved in poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1)-dependent replication gap filling as part of a backup pathway in the absence of OFs ligation. Altogether, our data suggest that CDK-mediated PNKP phosphorylation at T118 is important for its recruitment to ssDNA gaps to proceed with OFs ligation and its backup repairs via the gap-filling pathway to maintain genome stability.