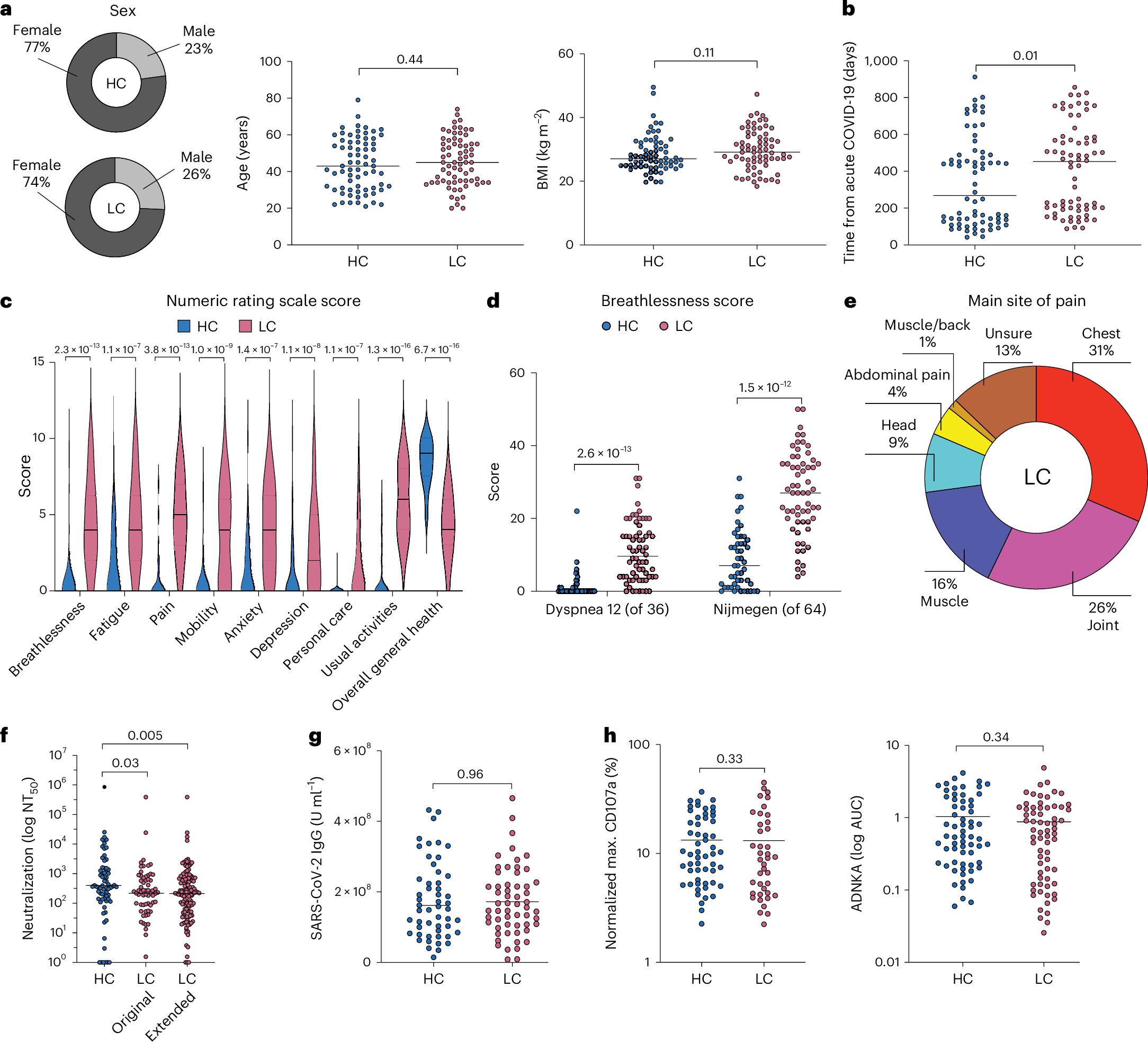
2025-04-30 中国科学院(CAS)
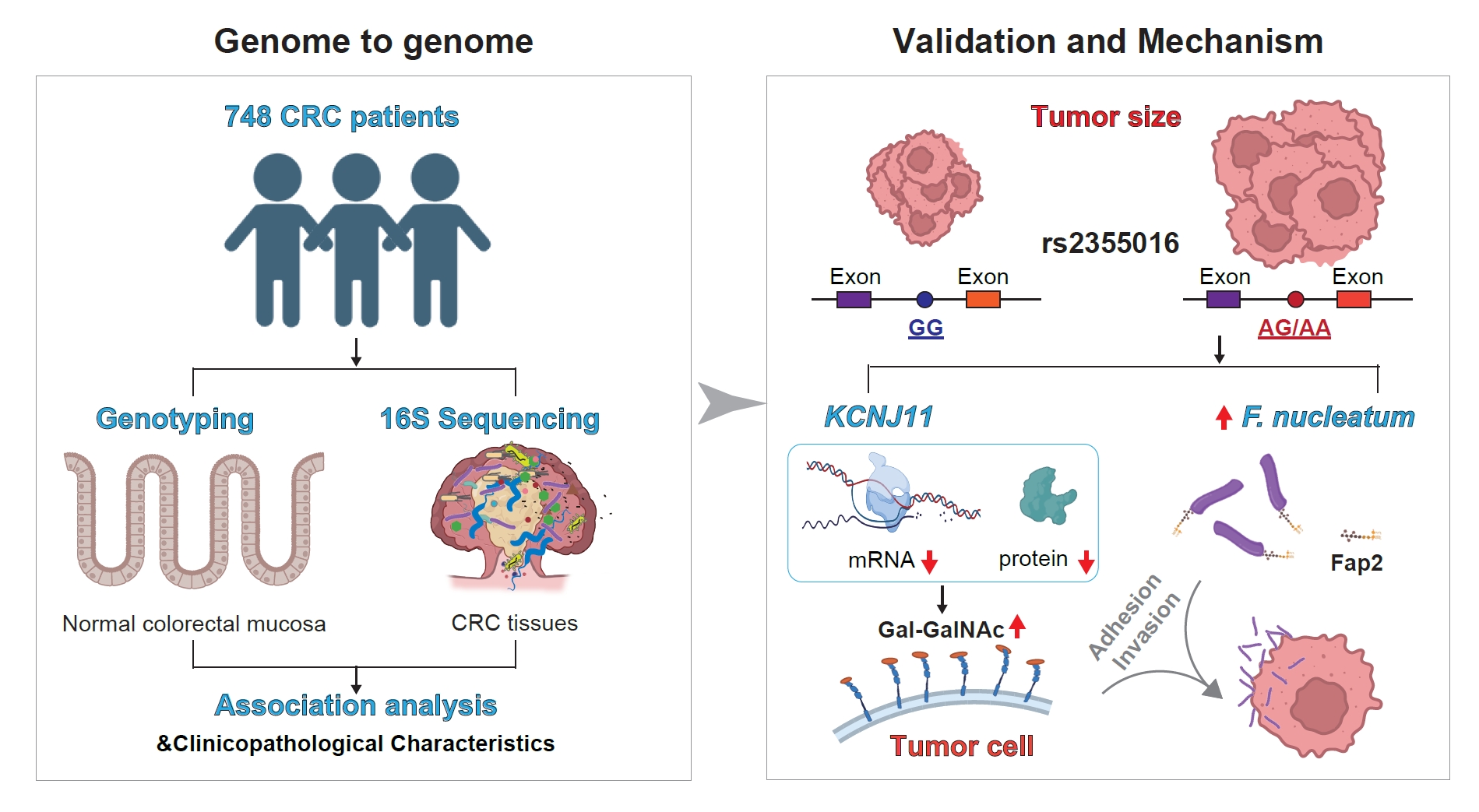 GWAS analyses show that a rs2355016 SNP in the KCNJ11 gene intron downregulates KCNJ11 expression, enhancing Gal-GalNAc on tumor cell surfaces, promoting adhesion and invasion of F. nuceatum through its Fap2 protein. (Image by Prof. WU’s team)
GWAS analyses show that a rs2355016 SNP in the KCNJ11 gene intron downregulates KCNJ11 expression, enhancing Gal-GalNAc on tumor cell surfaces, promoting adhesion and invasion of F. nuceatum through its Fap2 protein. (Image by Prof. WU’s team)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202504/t20250428_1042190.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1931312825001362
大腸癌の進行におけるヒト遺伝学と腫瘍内微生物叢の相互作用 An interplay between human genetics and intratumoral microbiota in the progression of colorectal cancer
Jing Yu, Yuxuan Liang, Qingrong Zhang, Hui Ding, Minghao Xie, Jingjing Zhang , Wenyan Hu, Sihua Xu, Yiyuan Xiao, Sha Xu, Rong Na, Baixing Wu, Jiaming Zhou, Haitao Chen
Cell Host & Microbe Published: April 29, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2025.04.003
Highlights
- SNP rs2355016 is correlated with the abundance of F. nucleatum
- Carriers of the rs2355016 A allele have lower expression levels of KCNJ11
- Downregulated KCNJ11 raises the level of Gal-GalNAc on the surface of CRC cells
- Elevated Gal-GalNAc enhances F. nucleatum binding by interacting with the Fap2 protein
Summary
Intratumoral microbiota plays a crucial role in cancer progression. However, the relationship between host genetics and intratumoral microbiota, as well as their interaction in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression, remains unclear. With 748 Chinese CRC patients enrolled from three cohorts, we find that the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs2355016, located in the intron of ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 (KCNJ11), is significantly associated with the abundance of Fusobacterium. Compared with the rs2355016 GG genotype, patients carrying the A allele exhibit downregulation of KCNJ11 and enrichment of Fusobacterium, which corresponds to accelerated proliferation and progression. Low expression of KCNJ11 can increase the level of galactose-N-acetyl-d-galactosamine (Gal-GalNAc) on the surface of CRC cells, thereby facilitating the binding of the Fap2 protein from F. nucleatum to Gal-GalNAc. This further enhances the adhesion and invasion of F. nucleatum and promotes CRC growth. Our study explores the interaction between intratumoral microbiota and SNPs in CRC patients, which will enhance our understanding of CRC proliferation.