2025-05-15 東京大学
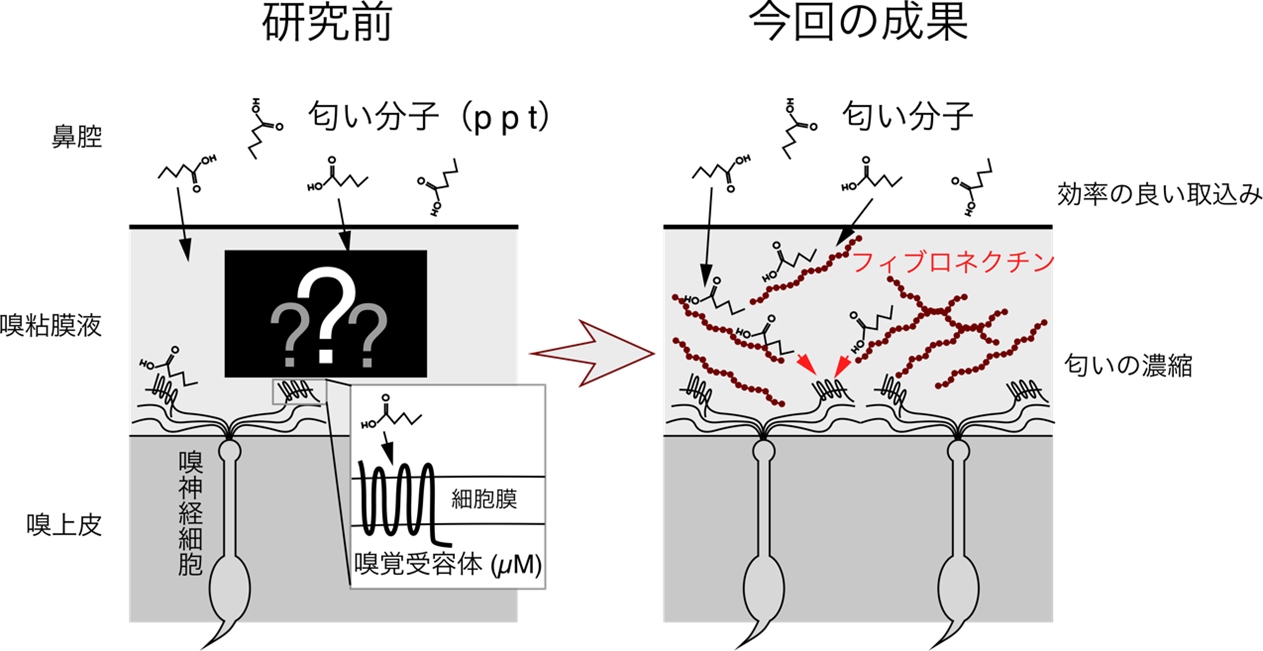
本研究で明らかになったフィブロネクチンの嗅覚感度上昇における役割
<関連情報>
- https://www.a.u-tokyo.ac.jp/topics/topics_20250515-1.html
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu7271
嗅粘膜中のフィブロネクチンは匂い物質に対する嗅覚受容体反応の感度を高める Fibronectin in the olfactory mucus increases sensitivity of olfactory receptor response to odorants
Stella Chapman, Kenji Kondo, Sayoko Ihara, Chiori Ijichi, […] , and Koji Sato
Science Advances Published:14 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adu7271
Abstract
Olfaction is a highly sensitive chemical detection system, but the origins of this sensitivity remain poorly understood. In terrestrial vertebrates, inhaled odorants diffuse through olfactory epithelial mucus (OEM) before activating olfactory receptors (ORs) on olfactory sensory neurons and initiating adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cAMP)–mediated signaling. Impaired OEM secretion is associated with impaired olfactory sensitivity in humans and mice, but it remains unclear whether OEM directly improves sensitivity and whether specific active factors exist. Here, using a cAMP imaging–based heterologous OR expression assay, we demonstrate that fibronectin from human OEM increases the sensitivity of OR response to odorant. Fibronectin application partially restores electrical olfactory response of the mouse olfactory epithelium after OEM removal. In humans, OEM fibronectin levels are significantly decreased in patients with idiopathic olfactory disorder. These findings shed light on the role of OEM fibronectin in olfaction and may lead to sensitivity-enhancing additives for odorant sensors and treatments for hyposmia.