2025-06-16 国立精神・神経医療研究センター
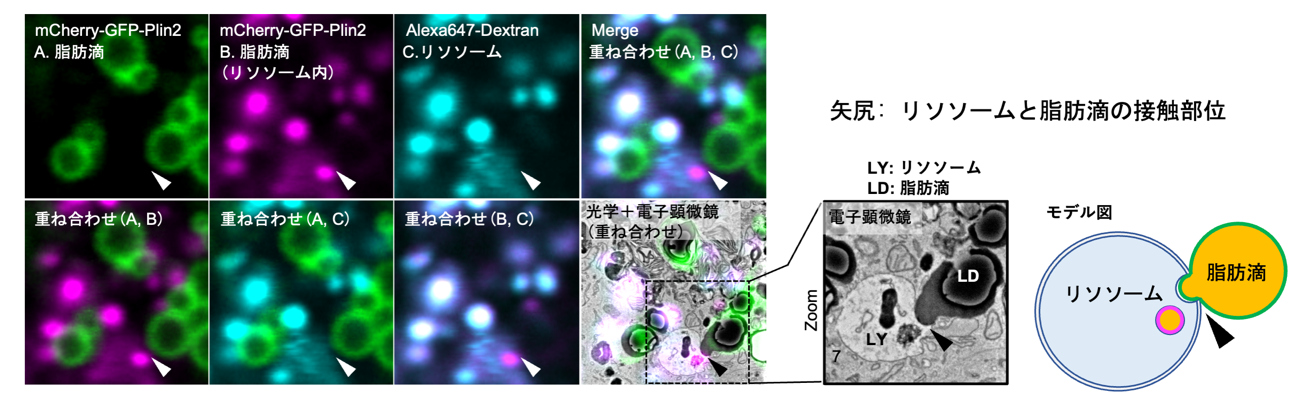
図1:光-電子相関顕微鏡により明らかとなった脂肪滴のミクロオートファジー2)(ミクロリポファジー)(本論文から改変引用)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncnp.go.jp/topics/detail.php?@uid=BaZdAD4DdihfRLZD
- https://www.ncnp.go.jp/press_search/images/files/PR_20250616.pdf
- https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00600-X
ライソゾーム膜タンパク質LAMP2Bはマイクロリポファジーを媒介し、肥満関連疾患を標的とする The lysosomal membrane protein LAMP2B mediates microlipophagy to target obesity-related disorders
Ryohei Sakai ∙ Shu Aizawa ∙ Hyeon-Cheol Lee-Okada ∙ … ∙ Tatsuo Mano ∙ Ikuko Koyama-Honda ∙ Tomohiro Kabuta
Cell Reports Published:June 10, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115829
Highlights
- LAMP2B mediates microlipophagy, not cytosolic lipolysis
- Interaction between LAMP2B and membrane lipids is required for this microlipophagy
- CLEM demonstrated direct lipid droplet uptake into lysosomes at contact sites
- LAMP2B overexpression in mice mitigates high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes
Summary
Lifestyle diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, are leading health problems, most of which are related to abnormal lipid metabolism. Lysosomes can degrade lipid droplets (LDs) via microautophagy, but the regulatory factors and physiological significance of this process are not fully understood. Here, we report the molecular mechanism and pathophysiological roles of microlipophagy, regulated by the lysosomal membrane protein LAMP2B. Our study reveals that LAMP2B interacts with phosphatidic acid, facilitating lysosomal-LD interactions and enhancing lipid hydrolysis via microlipophagy depending on endosomal sorting complexes required for transport. Correlative light and electron microscopy demonstrates direct LD uptake into lysosomes at contact sites. Moreover, LAMP2B overexpression in mice prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance, and adipose tissue inflammation; liver lipidomics analysis suggests enhanced triacylglycerol hydrolysis. Overall, the findings of this study elucidate the mechanism of microlipophagy, which could be promising for the treatment of obesity and related disorders.