2025-07-31 デューク大学
ChatGPT:

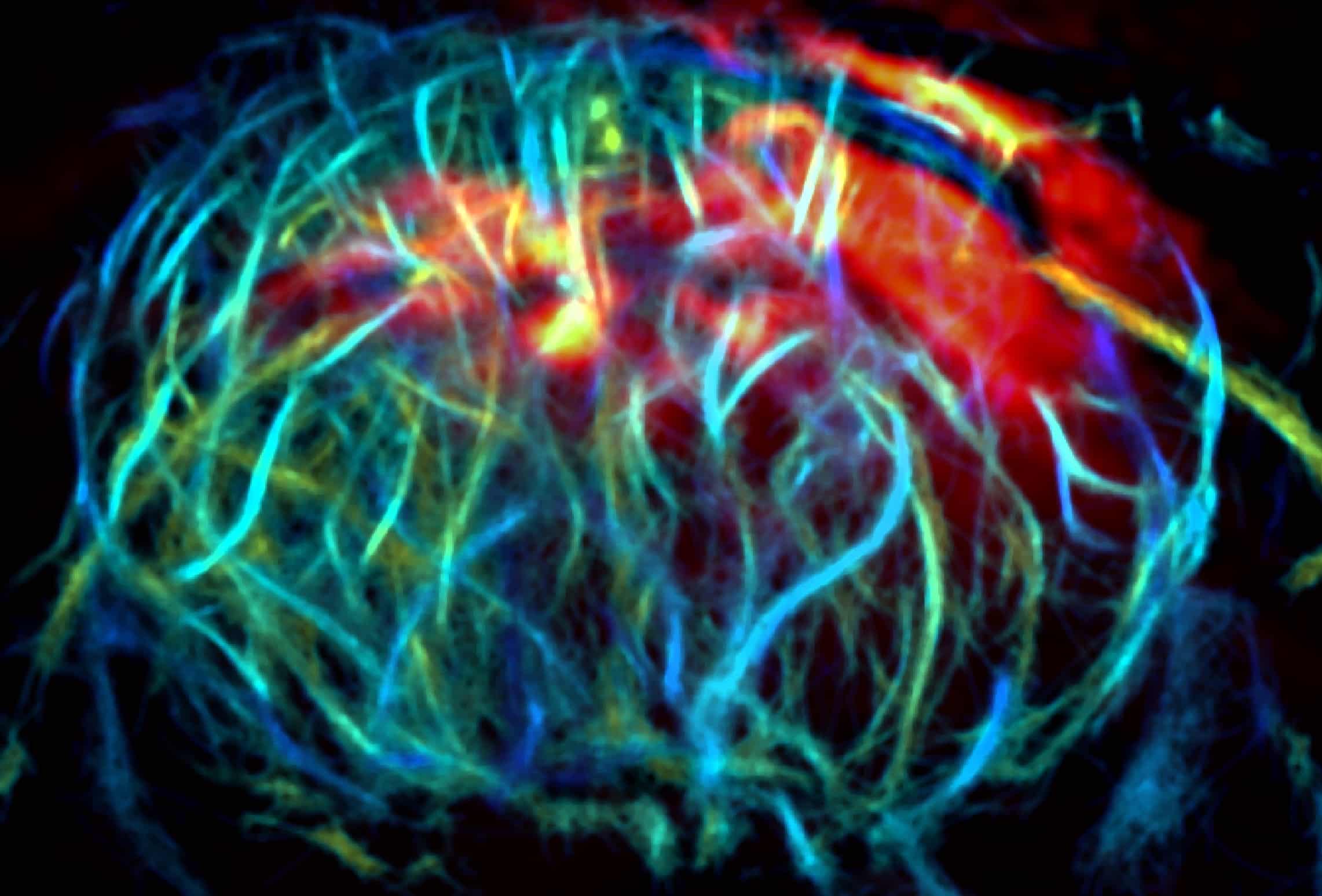
Credit: Junjie Yao and Vladislav V. Verkhusha
<関連情報>
- https://pratt.duke.edu/news/lightisensitive-molecules-for-deep-tissue-imaging/?cn-reloaded=1
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-61532-4
ビリベルジン還元酵素ノックアウトにより可能となった深部組織高感度マルチモーダル画像化と光遺伝学的操作 Deep-tissue high-sensitivity multimodal imaging and optogenetic manipulation enabled by biliverdin reductase knockout
Ludmila A. Kasatkina,Chenshuo Ma,Huaxin Sheng,Matthew Lowerison,Luca Menozzi,Mikhail Baloban,Yuqi Tang,Yirui Xu,Lucas Humayun,Tri Vu,Pengfei Song,Junjie Yao & Vladislav V. Verkhusha
Nature Communications Published:14 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-61532-4
Abstract
Performance of near-infrared probes and optogenetic tools derived from bacterial phytochromes is limited by availability of their biliverdin chromophore. To address this, we use a biliverdin reductase-A knock-out mouse model (Blvra-/-), which elevates endogenous biliverdin levels. We show that Blvra⁻/⁻ significantly enhances function of bacterial phytochrome-based systems. Light-controlled transcription using iLight optogenetic tool improves ~25-fold in Blvra-/- cells, compared to wild-type controls, and achieves ~100-fold activation in neurons. Light-induced insulin production in Blvra-/- mice reduces blood glucose by ~60% in diabetes model. To overcome depth limitations in imaging, we employ 3D photoacoustic, ultrasound, and two-photon fluorescence microscopy. This enables simultaneous photoacoustic imaging of DrBphP in neurons and super-resolution ultrasound localization microscopy of brain vasculature at depths of ~7 mm through intact scalp and skull. Two-photon microscopy achieves cellular resolution of miRFP720-expressing neurons at ~2.2 mm depth. Overall, Blvra-/- model represents powerful platform for improving efficacy of biliverdin-dependent tools for deep-tissue imaging and optogenetic manipulation.