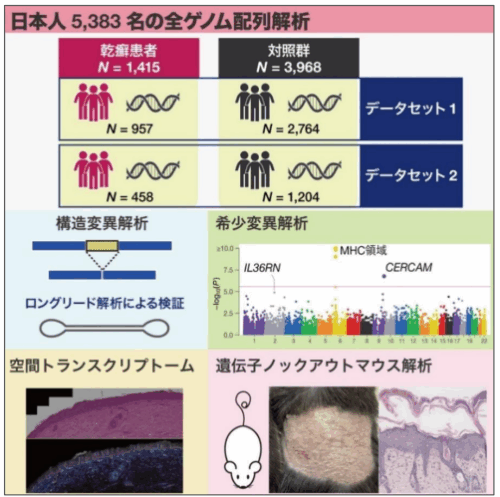
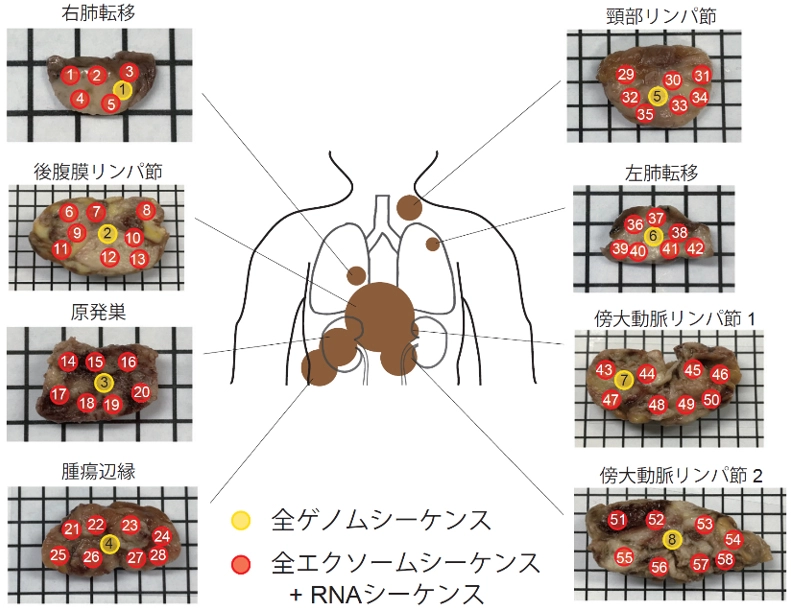
2025-08-29 東京科学大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/g2by6sekltq7
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2074&prevId=&key=68e7585f65a1b6dc3317b652f5ff5282.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/plphys/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/plphys/kiaf373/8241983
葉緑体エンベロープ局在性DLDG1は葉緑体ATP合成酵素を介したチラコイド膜間H⁺輸送を調節する Chloroplast envelope-localized DLDG1 modulates H+ translocation across thylakoid membranes via plastidial ATP synthase
Mai Duy Luu Trinh , Elham Esmailpourmoghadam , Ryoichi Sato , Chikahiro Miyake , Michael Palmgren , Shinji Masuda
Plant Physiology Published:26 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiaf373
Abstract
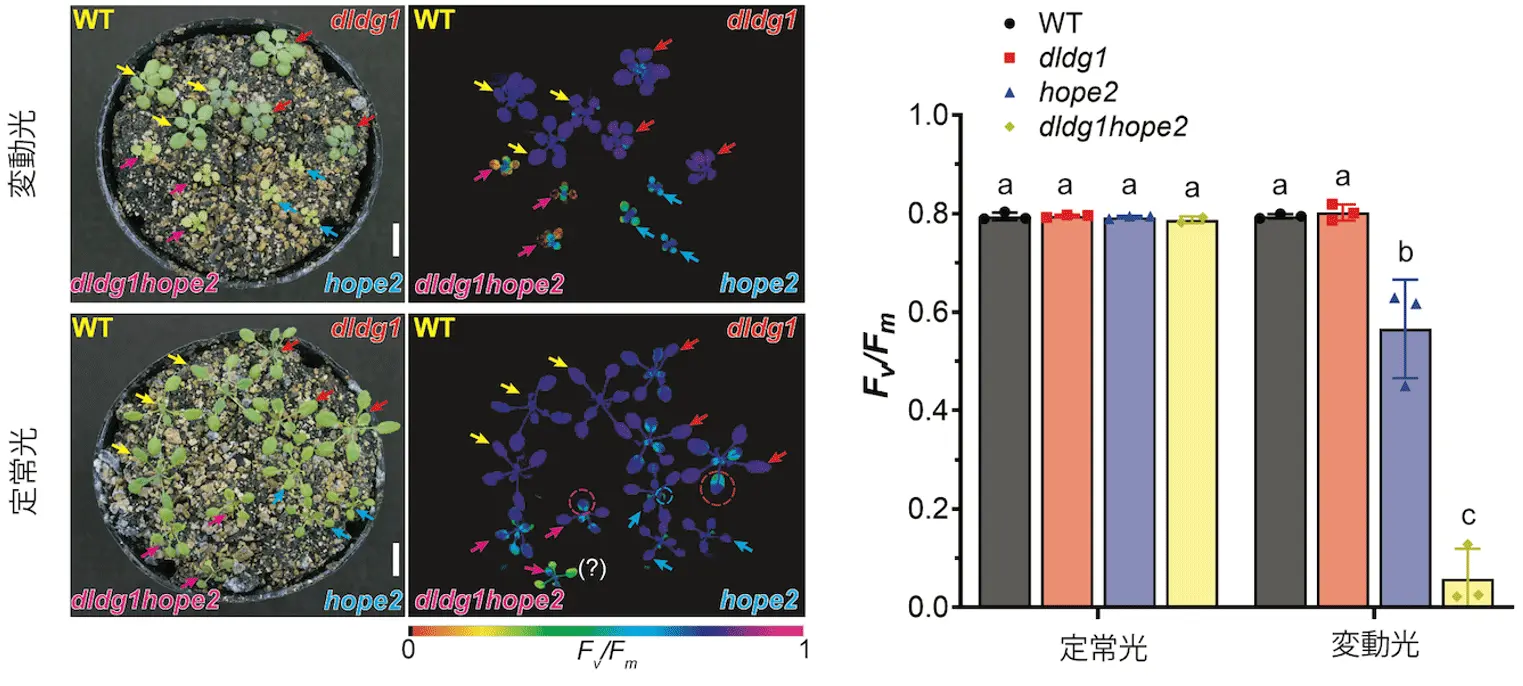
Land plants have evolved sophisticated regulatory mechanisms to precisely modulate electron flow during photosynthesis that is crucial for protecting the photosynthetic machinery and other cellular components from oxidative photodamage. Non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) serves as a major photoprotective mechanism, dissipating excess absorbed light energy as heat. The chloroplast protein DAY-LENGTH-DEPENDENT DELAYED-GREENING1 (DLDG1), which is specifically conserved in oxygenic phototrophs, plays a pivotal role in controlling NPQ by regulating H+ translocation across the chloroplast envelope membranes. The specific molecular mechanism by which DLDG1 influences NPQ and the H+ gradient across the thylakoid membrane (ΔpH) remains unclear, as DLDG1 localizes in the envelope membranes rather than the thylakoid membranes. Previous studies identified the hope2 (hunger for oxygen in photosynthetic electron transport reaction 2) mutant, which exhibits altered H+ conductivity (gH+) in the thylakoid membranes due to a point mutation in the chloroplast CFo-CF1 ATP synthase. To explore potential functional interactions between DLDG1 and CFo-CF1 ATP synthase, we generated a dldg1 hope2 double mutant in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Characterization of this double mutant revealed that the dldg1 null mutation partially compensated for the decreased NPQ and elevated gH+ observed in hope2. Our findings demonstrate a functional relationship between DLDG1 and CFo-CF1 ATP synthase in regulating ΔpH and photosynthetic electron flow from photosystem II to photosystem I under varying light intensities and CO2 concentrations. We conclude that DLDG1-dependent stromal pH regulation is important for H+ translocation across the thylakoid membranes through CFo-CF1 ATP synthase, thus supporting photosynthetic regulation and plant development under challenging environmental conditions.