2025-09-17 東京科学大学
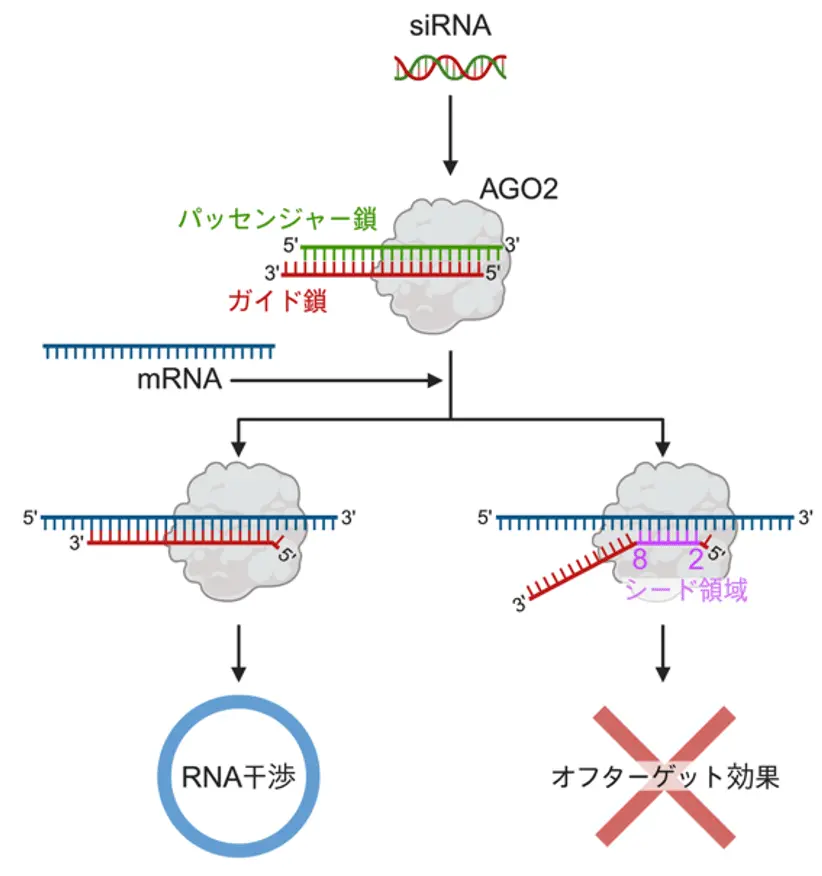
図1.siRNAのRNA干渉とオフターゲット効果
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/6m97gg927c9f
- https://www.cell.com/molecular-therapy-family/nucleic-acids/fulltext/S2162-2531(25)00247-1
化学修飾による構造歪みを表すsiRMSDパラメータはsiRNAのオフターゲット効果を予測する An siRMSD parameter of structural distortion induced by chemical modification is predictive of the off-target effect of siRNA
Seongjin An ∙ Kohei Nomura ∙ Yoshiaki Kobayashi ∙ Yasuaki Kimura ∙ Hiroshi Abe ∙ Kumiko Ui-Tei
Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acid Published:September 16, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102693
Abstract
We developed siRMSD, a predictive parameter for off-target effects induced by chemical modifications, to optimize siRNA therapeutics. In RNA interference, small interfering RNA (siRNA) suppresses gene function by degrading mRNA with perfect sequence complementarity, providing therapeutic potential through the targeted inhibition of disease-related genes. However, off-target effects on unintended mRNAs pose a significant challenge to clinical application. While chemical modifications improve nuclease stability and reduce off-target effects, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we show that structural distortions caused by chemical modifications determine off-target effects. Modifications, including 2′-O-methoxyethyl, 2′-O-methyl, and 2′-formamido, at positions 2–5 disrupted the A-form RNA duplex on argonaute 2, preventing stable binding to target mRNA. In contrast, modifications at positions 6–8 had minimal impact on off-target effect resulting from changes in thermodynamic stability.


