2025-10-22 マウントサイナイ医療システム(MSHS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/scientists-develop-a-way-to-track-donor-bacteria-after-fecal-microbiota-transplants
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-025-02164-8
糞便微生物移植後の株追跡のためのロングリードメタゲノミクス Long-read metagenomics for strain tracking after faecal microbiota transplant
Yu Fan,Mi Ni,Varun Aggarwala,Edward A. Mead,Magdalena Ksiezarek,Lei Cao,Michael A. Kamm,Thomas J. Borody,Sudarshan Paramsothy,Nadeem O. Kaakoush,Ari Grinspan,Jeremiah J. Faith & Gang Fang
Nature Microbiology Published:22 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-025-02164-8
Abstract
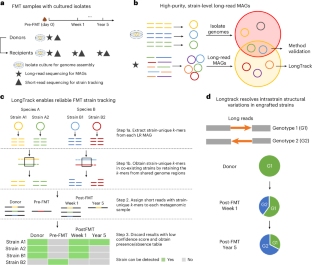
Accurate tracking of bacterial strains that stably engraft in faecal microbiota transplant (FMT) recipients is critical for understanding the determinants of strain engraftment, evaluating correlations with clinical outcomes and guiding the development of therapeutic consortia. While short-read sequencing has advanced FMT research, it faces challenges in strain-level de novo metagenomic assembly. Here we describe LongTrack, a method that uses long-read metagenomic assemblies for FMT strain tracking. LongTrack shows higher precision and specificity than short-read approaches, especially when multiple strains co-exist in the same sample. We uncovered 648 engrafted strains across six FMT cases involving patients with recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection and inflammatory bowel disease. Furthermore, long reads enabled assessment of the genomic and epigenomic stability of engrafted strains at the 5-year follow-up timepoint, revealing structural variations that may be associated with strain adaptation in a new host environment. Our findings support the use of long-read metagenomics to track microbial strains and their adaptations.