2025-11-10 千葉大学
本研究成果は、科学誌 Nature Communications にて2025年11月3日にオンライン公開されました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.chiba-u.ac.jp/news/research-collab/post_596.html
- https://www.chiba-u.ac.jp/news/files/pdf/1110_genom.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64659-6
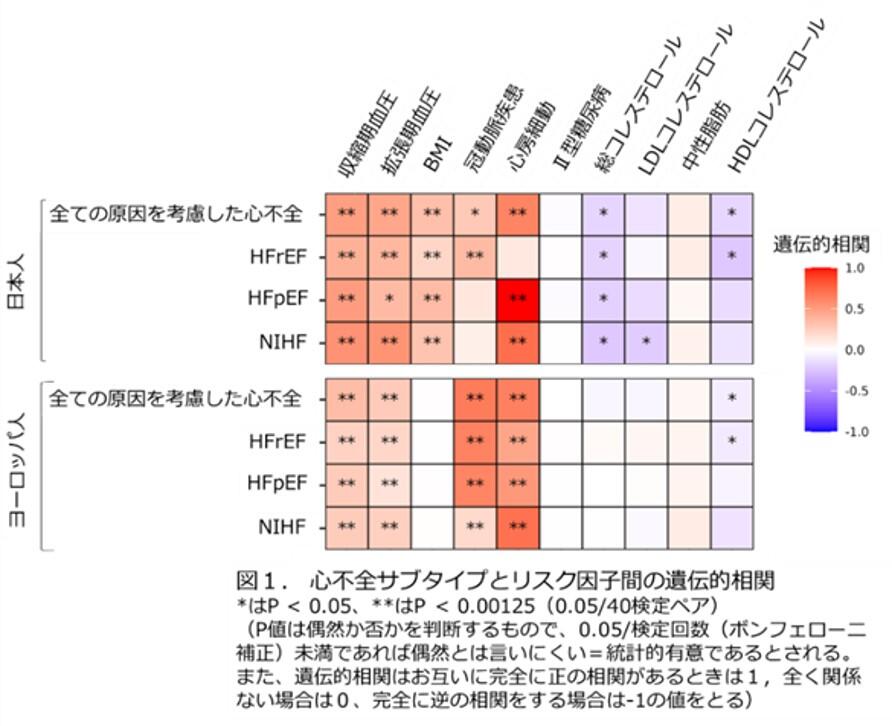
心不全のゲノムワイド解析により、疾患の異質性に関する知見が得られ、日本人集団における予後予測が可能になる Genome-wide analysis of heart failure yields insights into disease heterogeneity and enables prognostic prediction in the Japanese population
Nobuyuki Enzan,Kazuo Miyazawa,Satoshi Koyama,Ryo Kurosawa,Hirotaka Ieki,Hiroki Yoshida,Fumie Takechi,Masashi Fukuyama,Ryosuke Osako,Kohei Tomizuka,Xiaoxi Liu,Kouichi Ozaki,Yoshihiro Onouchi,the BioBank Japan Project,Koichi Matsuda,Yukihide Momozawa,Hiroyuki Aburatani,Yoichiro Kamatani,Takanori Yamaguchi,Hiroshi Akazawa,Koichi Node,Patrick T. Ellinor,Michael G. Levin,Scott M. Damrauer,… Kaoru Ito
Nature Communications Published:03 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64659-6
Abstract
To understand the genetic basis of heart failure (HF) in the Japanese population, we performed genome-wide association studies (GWASs) comprising 16,251 all-cause HF cases, 4254 HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) cases, 7154 HF with preserved ejection fraction cases, and 11,122 non-ischemic HF cases among 213,828 individuals and identified five novel loci. A subsequent cross-ancestry meta-analysis and multi-trait analysis of the GWAS data identified 19 novel loci in total, with 31 out of the 76 genome-wide significant loci associated with HFrEF despite its smaller sample size. Among these susceptibility loci, a common non-coding variant in TTN (rs1484116) was associated with reduced cardiac function and worse long-term mortality. We leveraged the HF meta-GWASs along with cardiac function-related GWASs to develop a polygenic risk score (PRS) for HF. The PRS successfully identified early-onset HF and those with an increased risk of long-term HF mortality. Our results shed light on the shared and distinct genetic basis of HF between Japanese and European populations and improve the clinical value of HF genetics.