2025-12-15 マウントサイナイ医療システム(MSHS)
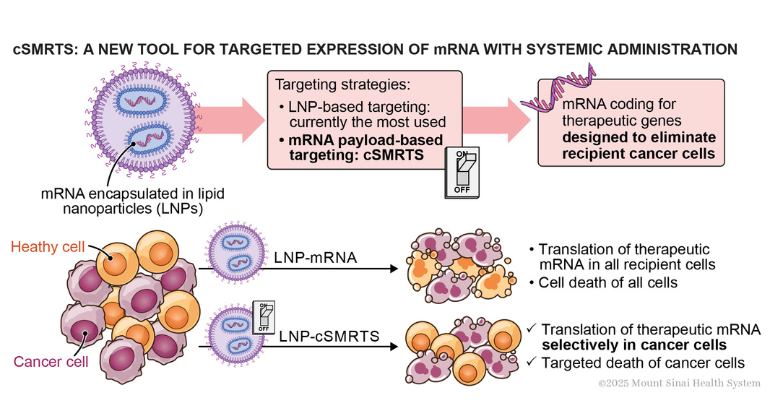
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai built an mRNA system that switches on therapeutic genes preferentially in targeted cells for greater precision and safety. Credit: Mount Sinai Health System
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/scientists-develop-a-smarter-mrna-therapy-that-knows-which-cells-to-target
- https://www.cell.com/molecular-therapy-family/molecular-therapy/abstract/S1525-0016(25)00954-2
腫瘍選択的mRNAシステムにより精密な癌治療が可能に A tumor-selective mRNA system enables precision cancer treatment
Magdalena M. Żak ∙ Jimeen Yoo ∙ Alberto Utrero-Rico ∙ … ∙ Ramon E. Parsons ∙ Filip K. Swirski ∙ Lior Zangi
Molecular Therapy Published:November 15, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.11.015
Abstract
mRNA has revolutionized vaccine development, demonstrating high efficacy and safety in COVID-19 vaccines, and is now being explored for broader therapeutic applications. However, while vaccines rely on widespread antigen expression, many therapeutic strategies—particularly in oncology—require precise, cell-selective gene expression. Here, we present the selective modified RNA translation system (SMRTS), a versatile, engineered mRNA system that enables targeted gene expression in specific cell populations. As a proof of concept, we developed cancer-specific variants, bcSMRTS and ccSMRTS, for breast and colon cancer, respectively. Systemic delivery of lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-encapsulated SMRTS constructs yielded a 114-fold and 141-fold increase in tumor-specific expression in 4T1 and MC-38 models, respectively, while reducing off-target expression by over 380-fold. Therapeutic deployment of Pten ccSMRTS suppressed tumor growth by 45%, and combination with modRNA-derived anti-checkpoint inhibitor antibodies (modRNabs) resulted in up to 93% tumor inhibition. Beyond oncology, SMRTS introduces a novel mRNA tool, providing a versatile system for cell-selective gene expression. By expanding the mRNA therapeutics toolbox, SMRTS paves the way for precise mRNA-based interventions across a wide range of disease settings.