2025-12-15 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202512/t20251218_1137811.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64987-7
視覚認識は、注意ネットワークにおける抑制性神経調節を強化することで、注意のサンプリングを鋭敏化し、加速させる Visual awareness sharpens and accelerates attentional sampling through enhancing inhibitory neural modulation in the attention network
Fang Yang,Peijun Yuan,Li Shen,Ke Zhou,Sheng He & Yi Jiang
Nature Communications Published:17 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64987-7
Abstract
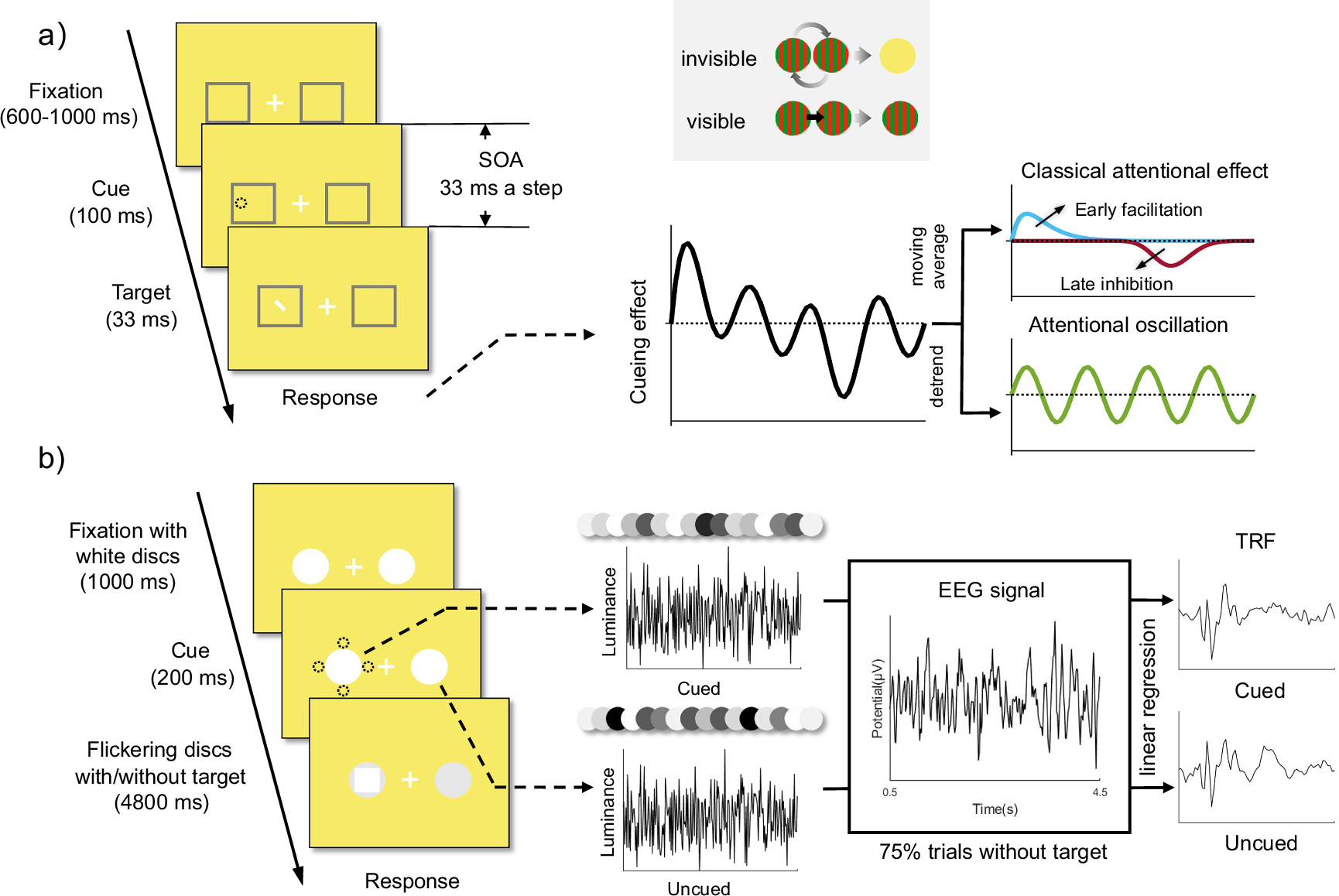
Attentional sampling, orchestrated by neural oscillations within the frontoparietal attention network, sequentially focuses on stimuli in a dynamic pattern, thereby enhancing the efficiency of attentional selection. However, the role of conscious awareness in this default attentional process remains largely unexplored. Here, we employed the Chromatic Flicker Fusion (CFF) method to render attentional cues invisible and investigated how cue awareness modulates attentional sampling. Using a high-temporal-resolution behavioral paradigm and electroencephalography (EEG) combined with the temporal response function (TRF) approach, we found that both visible and invisible cues induced rhythmic behavioral sampling and reset connectivity between the frontal and right occipito-parietal regions, indicating that attention samples rhythmically regardless of cue awareness. Crucially, visible cues not only elicited stronger behavioral inhibition and enhanced neural alpha activity, but also triggered faster attentional sampling (~8 Hz vs. ~4 Hz) and higher-frequency frontoparietal coupling (alpha vs. theta band). These findings demonstrate that the conscious representation of attentional cues influences inhibitory neural responses within the frontoparietal attention network and modulates the attentional sampling process.


