2022-04-29 マックス・プランク研究所
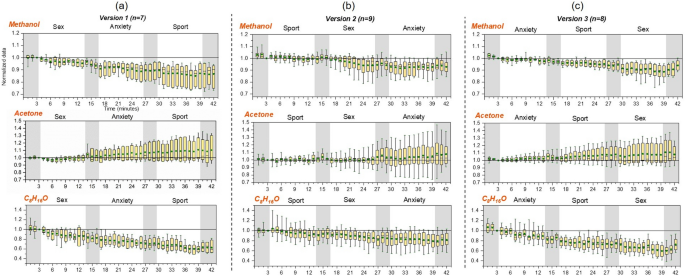
・この研究によれば、性的に興奮した人の呼気には、揮発性分子の特徴的なシグネチャーが見られるという。被験者が吐き出すイソプレンと二酸化炭素の量は少なく、ある種の神経伝達物質の分解産物の濃度が上昇していた。
・研究者によると、この発見は、臨床的に性的興奮をよりよく評価するのに役立ち、その結果、性的障害の評価に貢献する可能性があるという。
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/18577820/0429-chem-heisser-atem-152990-x?c=2249
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-10325-6
ヒトにおける性的覚醒のブレスケミカルマーカー Breath chemical markers of sexual arousal in humans
N. Wang,G. Pugliese,M. Carrito,C. Moura,P. Vasconcelos,N. Cera,M. Li,P. Nobre,J. R. Georgiadis,J. K. Schubert & J. Williams
Scientific Reports Published: 15 April 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10325-6
Abstract
The chemical composition of exhaled breath was examined for volatile organic compound (VOC) indicators of sexual arousal in human beings. Participants (12-male, 12-female) were shown a randomized series of three emotion-inducing 10-min film clips interspersed with 3-min neutral film clips. The films caused different arousals: sports film (positive-nonsexual); horror film (negative-nonsexual); and erotic (sexual) that were monitored with physiological measurements including genital response and temperature. Simultaneously the breath was monitored for VOC and CO2. While some breath compounds (methanol and acetone) changed uniformly irrespective of the film order, several compounds did show significant arousal associated changes. For both genders CO2 and isoprene decreased in the sex clip. Some male individuals showed particularly strong increases of indole, phenol and cresol coincident with sexual arousal that decreased rapidly afterwards. These VOCs are degradation products of tyrosine and tryptophan, precursors for dopamine, noradrenalin, and serotonin, and therefore represent potential breath markers of sexual arousal.