アルツハイマー病の治療に役立つ新しい無膜オルガネラを発見、その特性を解明 Researchers discover and characterize a novel membraneless organelle that could play a role in Alzheimer’s treatment
2022-06-16 カリフォルニア大学サンタバーバラ校(UCSB)
<関連情報>
- https://www.news.ucsb.edu/2022/020659/cellular-cleanup
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-30751-4
ストレスがクライアントをBAG2ユビキチン非依存性分解コンデンセート経由でプロテアソームへ導く Stress routes clients to the proteasome via a BAG2 ubiquitin-independent degradation condensate
Daniel C. Carrettiero,Maria C. Almeida,Andrew P. Longhini,Jennifer N. Rauch,Dasol Han,Xuemei Zhang,Saeed Najafi,Jason E. Gestwicki & Kenneth S. Kosik
Nature Communications Published:02 June 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30751-4
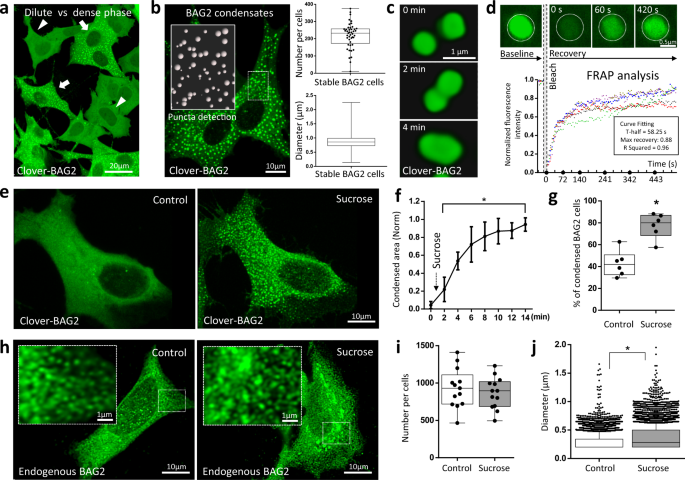
Abstract
The formation of membraneless organelles can be a proteotoxic stress control mechanism that locally condenses a set of components capable of mediating protein degradation decisions. The breadth of mechanisms by which cells respond to stressors and form specific functional types of membraneless organelles, is incompletely understood. We found that Bcl2-associated athanogene 2 (BAG2) marks a distinct phase-separated membraneless organelle, triggered by several forms of stress, particularly hyper-osmotic stress. Distinct from well-known condensates such as stress granules and processing bodies, BAG2-containing granules lack RNA, lack ubiquitin and promote client degradation in a ubiquitin-independent manner via the 20S proteasome. These organelles protect the viability of cells from stress and can traffic to the client protein, in the case of Tau protein, on the microtubule. Components of these ubiquitin-independent degradation organelles include the chaperone HSP-70 and the 20S proteasome activated by members of the PA28 (PMSE) family. BAG2 condensates did not co-localize with LAMP-1 or p62/SQSTM1. When the proteasome is inhibited, BAG2 condensates and the autophagy markers traffic to an aggresome-like structure.