2023-05-09 リンショーピング大学
◆スウェーデンのリンシェーピング大学とスコーヴデ大学の研究者たちは、状況がオキシトシンのレベルに与える影響について調査し、その瞬間だけでなく、後にも影響を与えることが明らかになった。
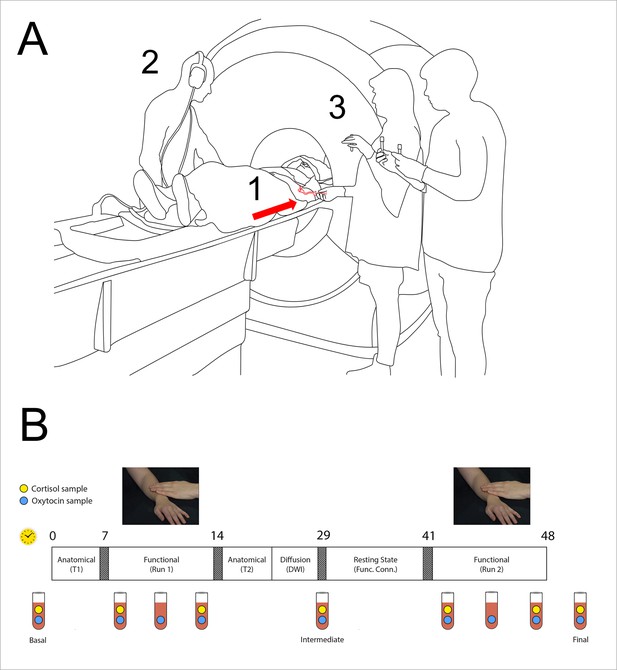
◆本研究は、女性42名を対象に、パートナーに触れられた際の脳内活動を検査することで実施された。そして、異性が触れた場合とパートナーが触れた場合とでオキシトシンの変化を比較し、状況によってホルモンレベルが変化することが判明した。
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/the-brain-reacts-differently-to-touch-depending-on-context
- https://elifesciences.org/articles/81197
ヒトの内因性オキシトシンとその神経相関は、最近の社会的文脈に基づく社会的接触への適応的な反応を示す Human endogenous oxytocin and its neural correlates show adaptive responses to social touch based on recent social context
Linda Handlin,Giovanni Novembre,Helene Lindholm,Robin Kämpe,Elisabeth Paul,India Morrison
eLife Published: May 9, 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.81197
Abstract
Both oxytocin (OT) and touch are key mediators of social attachment. In rodents, tactile stimulation elicits the endogenous release of OT, potentially facilitating attachment and other forms of prosocial behavior, yet the relationship between endogenous OT and neural modulation remains unexplored in humans. Using a serial sampling of plasma hormone levels during functional neuroimaging across two successive social interactions, we show that contextual circumstances of social touch influence not only current hormonal and brain responses but also later responses. Namely, touch from a male to his female romantic partner enhanced her subsequent OT release for touch from an unfamiliar stranger, yet females’ OT responses to partner touch were dampened following stranger touch. Hypothalamus and dorsal raphe activation reflected plasma OT changes during the initial social interaction. In the subsequent interaction, precuneus and parietal-temporal cortex pathways tracked time- and context-dependent variables in an OT-dependent manner. This OT-dependent cortical modulation included a region of the medial prefrontal cortex that also covaried with plasma cortisol, suggesting an influence on stress responses. These findings demonstrate that modulation between hormones and the brain during human social interactions can flexibly adapt to features of social context over time.