重要なタンパク質がなければウイルスは人に感染しない Without key proteins, virus cannot infect people
2023-09-13 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
◆COVID-19ウイルスの複製に必要なタンパク質Nは、その仕事をするために人間の細胞の助けを必要とします。この発見により、ウイルスの複製を妨げる方法が開発され、新たな抗ウイルス薬の可能性が浮上しています。現在、最も効果的なCOVID-19治療薬はPaxlovidですが、感染後3日以内に使用する必要があります。この発見に基づいた新しい薬は、感染のあらゆる段階で患者に役立つ可能性があります。ウイルス間の類似性から、新しい抗ウイルス薬の新たなクラスが開発される可能性があり、Liao教授はその実現に5年かかると推定しています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2023/09/13/scientists-uncover-covids-weakness
- https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/15/7/1600
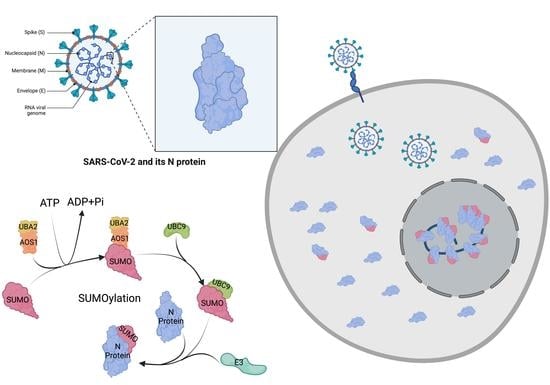
SARS-CoV-2ヌクレオカプシド蛋白質のヒト翻訳後SUMO修飾は、それ自身との相互作用親和性を高め、核内移行に重要な役割を果たす Human Post-Translational SUMOylation Modification of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Enhances Its Interaction Affinity with Itself and Plays a Critical Role in Its Nuclear Translocation
Vipul Madahar,Runrui Dang,Quanqing Zhang,Chuchu Liu,Victor G. J. Rodgers andJiayu Liao
Viruses Published: 21 July 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071600
Abstract
Viruses, such as Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), infect hosts and take advantage of host cellular machinery for genome replication and new virion production. Identifying and elucidating host pathways for viral infection is critical for understanding the development of the viral life cycle and novel therapeutics. The SARS-CoV-2 N protein is critical for viral RNA (vRNA) genome packaging in new virion formation. Using our quantitative Förster energy transfer/Mass spectrometry (qFRET/MS) coupled method and immunofluorescence imaging, we identified three SUMOylation sites of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. We found that (1) Small Ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification in Nucleocapsid (N) protein interaction affinity increased, leading to enhanced oligomerization of the N protein; (2) one of the identified SUMOylation sites, K65, is critical for its nuclear translocation. These results suggest that the host human SUMOylation pathway may be critical for N protein functions in viral replication and pathology in vivo. Thus, blocking essential host pathways could provide a novel strategy for future anti-viral therapeutics development, such as for SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses.