2024-05-22 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
◆新しいコーティングは、水を迅速に吸収し、強力な結合を形成するハイドロゲル接着剤を使用しています。この技術により、ペースメーカーのような医療機器が長期間機能を維持し、瘢痕組織の形成を防ぐことができます。
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2024/adhesive-coatings-can-prevent-scarring-around-medical-implants-0522
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07426-9
多様な臓器における粘着性抗線維化インターフェース Adhesive anti-fibrotic interfaces on diverse organs
Jingjing Wu,Jue Deng,Georgios Theocharidis,Tiffany L. Sarrafian,Leigh G. Griffiths,Roderick T. Bronson,Aristidis Veves,Jianzhu Chen,Hyunwoo Yuk & Xuanhe Zhao
Nature Published:22 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07426-9
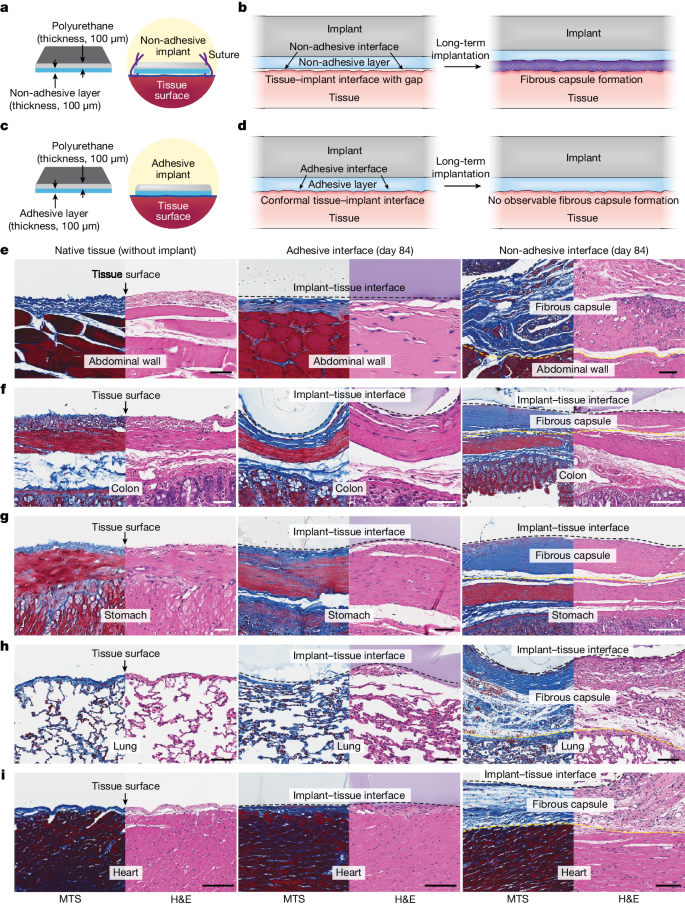
Abstract
Implanted biomaterials and devices face compromised functionality and efficacy in the long term owing to foreign body reactions and subsequent formation of fibrous capsules at the implant–tissue interfaces1,2,3,4. Here we demonstrate that an adhesive implant–tissue interface can mitigate fibrous capsule formation in diverse animal models, including rats, mice, humanized mice and pigs, by reducing the level of infiltration of inflammatory cells into the adhesive implant–tissue interface compared to the non-adhesive implant–tissue interface. Histological analysis shows that the adhesive implant–tissue interface does not form observable fibrous capsules on diverse organs, including the abdominal wall, colon, stomach, lung and heart, over 12 weeks in vivo. In vitro protein adsorption, multiplex Luminex assays, quantitative PCR, immunofluorescence analysis and RNA sequencing are additionally carried out to validate the hypothesis. We further demonstrate long-term bidirectional electrical communication enabled by implantable electrodes with an adhesive interface over 12 weeks in a rat model in vivo. These findings may offer a promising strategy for long-term anti-fibrotic implant–tissue interfaces.


