2024-06-28 リンショーピング大学
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/a-liver-biopsy-may-predict-spread-of-pancreatic-cancer-
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03075-7
早期膵癌の転移転帰予測のための転移前肝のマルチパラメトリックアトラス Multi-parametric atlas of the pre-metastatic liver for prediction of metastatic outcome in early-stage pancreatic cancer
Linda Bojmar,Constantinos P. Zambirinis,Jonathan M. Hernandez,Jayasree Chakraborty,Lee Shaashua,Junbum Kim,Kofi Ennu Johnson,Samer Hanna,Gokce Askan,Jonas Burman,Hiranmayi Ravichandran,Jian Zheng,Joshua S. Jolissaint,Rami Srouji,Yi Song,Ankur Choubey,Han Sang Kim,Michele Cioffi,Elke van Beek,Carlie Sigel,Jose Jessurun,Paulina Velasco Riestra,Hakon Blomstrand,Carolin Jönsson,… David Lyden
Nature Medicine Published:28 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03075-7
Abstract
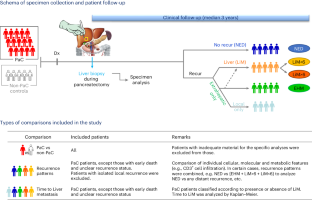
Metastasis occurs frequently after resection of pancreatic cancer (PaC). In this study, we hypothesized that multi-parametric analysis of pre-metastatic liver biopsies would classify patients according to their metastatic risk, timing and organ site. Liver biopsies obtained during pancreatectomy from 49 patients with localized PaC and 19 control patients with non-cancerous pancreatic lesions were analyzed, combining metabolomic, tissue and single-cell transcriptomics and multiplex imaging approaches. Patients were followed prospectively (median 3 years) and classified into four recurrence groups; early (<6 months after resection) or late (>6 months after resection) liver metastasis (LiM); extrahepatic metastasis (EHM); and disease-free survivors (no evidence of disease (NED)). Overall, PaC livers exhibited signs of augmented inflammation compared to controls. Enrichment of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), Ki-67 upregulation and decreased liver creatine significantly distinguished those with future metastasis from NED. Patients with future LiM were characterized by scant T cell lobular infiltration, less steatosis and higher levels of citrullinated H3 compared to patients who developed EHM, who had overexpression of interferon target genes (MX1 and NR1D1) and an increase of CD11B+ natural killer (NK) cells. Upregulation of sortilin-1 and prominent NETs, together with the lack of T cells and a reduction in CD11B+ NK cells, differentiated patients with early-onset LiM from those with late-onset LiM. Liver profiles of NED closely resembled those of controls. Using the above parameters, a machine-learning-based model was developed that successfully predicted the metastatic outcome at the time of surgery with 78% accuracy. Therefore, multi-parametric profiling of liver biopsies at the time of PaC diagnosis may determine metastatic risk and organotropism and guide clinical stratification for optimal treatment selection.