2024-09-16 ヒューストン大学(UH)
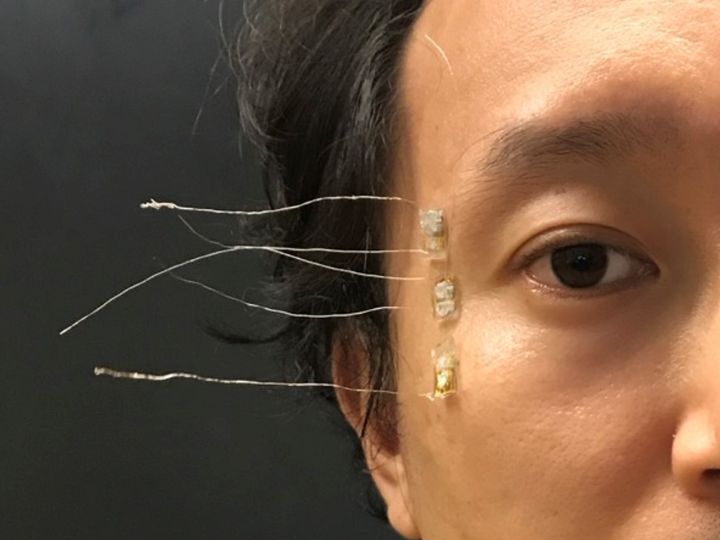
New wearable sensors, developed by UH engineers, examine eye movement to assess brain disorders or damage to the brain.
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2024/september/09162024-ryou-wearable-eye-sensors.php
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adhm.202303581
眼球運動の連続的かつ安全なモニタリングのための皮膚装着型配列圧電センサー Skin-Attached Arrayed Piezoelectric Sensors for Continuous and Safe Monitoring of Oculomotor Movements
Nam-In Kim, Jie Chen, Weijie Wang, Ja-Yeon Kim, Min-Ki Kwon, Mina Moradnia, Sara Pouladi, Jae-Hyun Ryou
Advanced Healthcare Materials Published: 22 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202303581
Abstract
Abnormal oculomotor movements are known to be linked to various types of brain disorders, physical/mental shocks to the brain, and other neurological disorders, hence its monitoring can be developed into a simple but effective diagnostic tool. To overcome the limitations in the current eye-tracking system and electrooculography, a piezoelectric arrayed sensor system is developed using single-crystalline III-N thin-film transducers, which offers advantages of mechanical flexibility, biocompatibility, and high electromechanical conversion, for continuous monitoring of oculomotor movements by skin-attachable, safe, and highly sensitive sensors. The flexible piezoelectric eye movement sensor array (F-PEMSA), consisting of three transducers, is attached to the face temple area where it can be comfortably wearable and can detect the muscles’ activity associated with the eye motions. Output voltages from upper, mid, and lower sensors (transducers) on different temple areas generate discernable patterns of output voltage signals with different combinations of positive/negative signs and their relative magnitudes for the various movements of eyeballs including 8 directional (lateral, vertical, and diagonal) and two rotational movements, which enable various types of saccade and pursuit tests. The F-PEMSA can be used in clinical studies on the brain-eye relationship to evaluate the functional integrity of multiple brain systems and cognitive processes.