2024-10-08 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/key-molecule-in-wound-healing-identified
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-52783-8
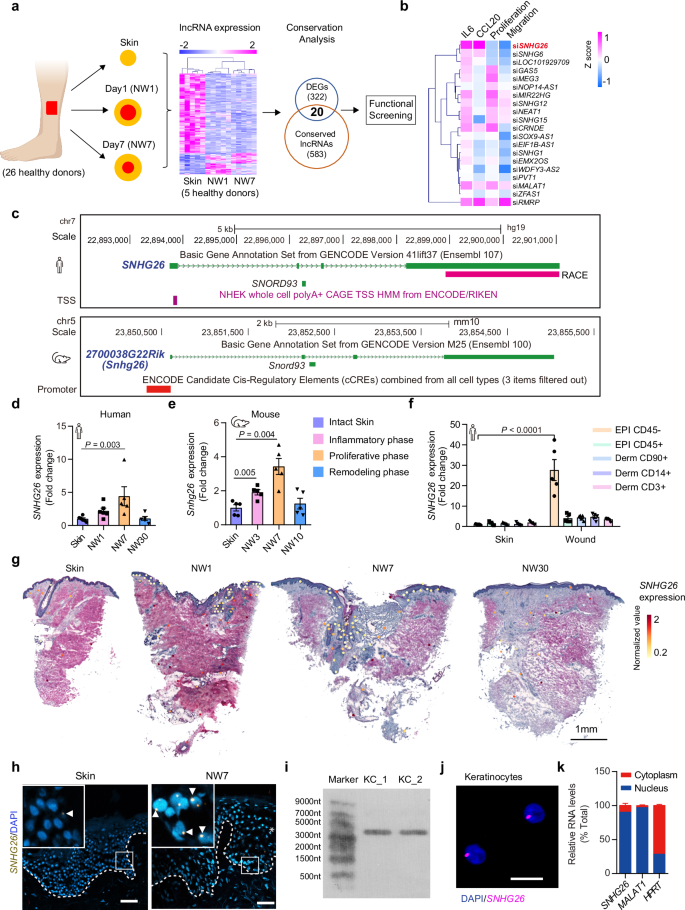
lncRNAのSNHG26が創傷治癒におけるケラチノサイト前駆細胞の炎症状態から増殖状態への移行を促進する The lncRNA SNHG26 drives the inflammatory-to-proliferative state transition of keratinocyte progenitor cells during wound healing
Dongqing Li,Zhuang Liu,Letian Zhang,Xiaowei Bian,Jianmin Wu,Li Li,Yongjian Chen,Lihua Luo,Ling Pan,Lingzhuo Kong,Yunting Xiao,Jiating Wang,Xiya Zhang,Wang Wang,Maria Toma,Minna Piipponen,Pehr Sommar & Ning Xu Landén
Nature Communications Published:05 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-52783-8
Abstract
The cell transition from an inflammatory phase to a subsequent proliferative phase is crucial for wound healing, yet the driving mechanism remains unclear. By profiling lncRNA expression changes during human skin wound healing and screening lncRNA functions, we identify SNHG26 as a pivotal regulator in keratinocyte progenitors underpinning this phase transition. Snhg26-deficient mice exhibit impaired wound repair characterized by delayed re-epithelization accompanied by exacerbated inflammation. Single-cell transcriptome analysis combined with gain-of-function and loss-of-function of SNHG26 in vitro and ex vivo reveals its specific role in facilitating inflammatory-to-proliferative state transition of keratinocyte progenitors. A mechanistic study unravels that SNHG26 interacts with and relocates the transcription factor ILF2 from inflammatory genomic loci, such as JUN, IL6, IL8, and CCL20, to the genomic locus of LAMB3. Collectively, our findings suggest that lncRNAs play cardinal roles in expediting tissue repair and regeneration and may constitute an invaluable reservoir of therapeutic targets in reparative medicine.