2024-11-14 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2024/11/14/uc-irvine-led-study-reveals-new-insights-into-how-we-navigate-space-and-store-memories/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-024-02819-8
空間認知への寄与に差のある後頭葉皮質の投射特異的回路 Projection-specific circuits of retrosplenial cortex with differential contributions to spatial cognition
Xiaoxiao Lin,Ali Ghafuri,Xiaojun Chen,Musab Kazmi,Douglas A. Nitz & Xiangmin Xu
Molecular Psychiatry Published:07 November 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-024-02819-8
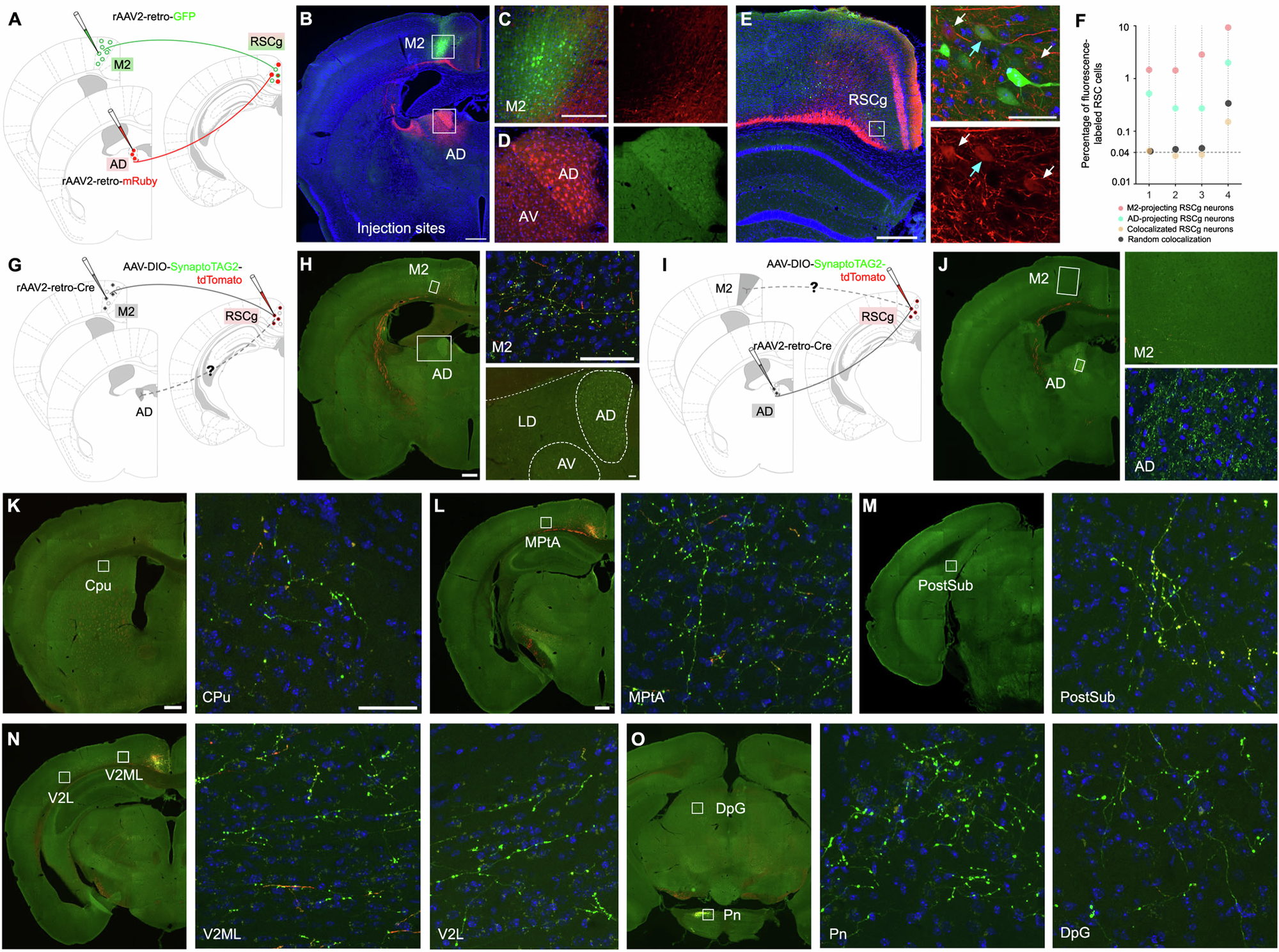
Abstract
Retrosplenial cortex (RSC) is a brain region involved in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. It has reciprocal connections with a diverse set of cortical and subcortical brain regions, but the afferent structure and behavioral function of circuits defined by its projection-specific sub-populations have yet to be determined. The corticocortical connections between RSC and secondary motor cortex (M2), as well as corticothalamic connections between RSC and anterodorsal thalamus (AD) have been hypothesized to function as semi-independent, but parallel pathways that impact spatial information processing in distinct ways. We used retrograde and anterograde viral tracers and monosynaptic retrograde rabies virus to quantitatively characterize and compare the afferent and efferent distributions of retrosplenial neuron sub-populations projecting to M2 and AD. AD-projecting and M2-projecting RSC neurons overlap in their collateral projections to other brain regions, but not in their projections to M2 and AD, respectively. Compared with AD-projecting RSC neurons, M2-projecting RSC neurons received much greater afferent input from the dorsal subiculum, AD, lateral dorsal and lateral posterior thalamus, and somatosensory cortex. AD-projecting RSC neurons received greater input from the anterior cingulate cortex and medial septum. We performed chemogenetic inhibition of M2- and AD-projecting RSC neurons and examined its impact on object-location memory, object-recognition, open-field exploration, and place-action association. Our findings indicate that inhibition of M2-projecting RSC neurons impairs object location memory as well as place-action association, while the RSC to AD pathway impacts only object-location memory. The findings indicate that RSC is composed of semi-independent circuits distinguishable by their afferent/efferent distributions and differing in the cognitive functions to which they contribute.